Why Are Ink Cartridges So Expensive? This question plagues many printer owners. At WHY.EDU.VN, we aim to provide a comprehensive explanation of the high costs associated with printer ink, exploring factors from research and development to business models, and provide you with solutions like exploring compatible cartridges and understanding ink volume. Let’s dive into this complex topic and uncover why ink costs can sometimes exceed the price of the printer itself, covering ink pricing, printer supplies, and cartridge costs.
1. The Razor and Blades Business Model
The primary reason for the high cost of ink cartridges lies in the business model employed by printer manufacturers. Companies like HP, Epson, Canon, and Brother often sell their printers at or below cost. Their primary profit source isn’t the hardware itself but the replacement ink cartridges.
1.1 Printers Sold at a Loss
Many printer companies operate on a “razor and blades” model. Think of it this way: you buy a razor (the printer) relatively cheaply. The company then makes its money on the replacement blades (ink cartridges), which you need to keep buying. This model allows companies to attract customers with low initial costs, knowing they’ll recoup their investment through ongoing ink sales.
1.2 OEM vs. Third-Party Cartridges
Manufacturers encourage consumers to stick with genuine Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) cartridges. While compatible and remanufactured third-party products exist, they may not offer the same reliability. This preference for OEM cartridges allows manufacturers to maintain higher prices. According to a study by Keypoint Intelligence, OEM cartridges generally provide better print quality and reliability compared to third-party options.
2. Research and Development (R&D) Costs
Printer manufacturers invest heavily in research and development to create advanced ink formulations and cartridge technologies. These costs are then factored into the price of ink cartridges.
2.1 Significant Investments
HP, for instance, claims to invest billions of dollars annually in ink research and development. This includes developing new ink formulas, improving print quality, and creating innovative cartridge designs. They hold thousands of patents related to imaging and printing, demonstrating the complexity and cost of this research.
2.2 Specialized Formulations
Inks are specially formulated for each brand and type of printer. This specialization ensures optimal performance and print quality. The cost of developing these specialized formulations contributes to the overall price of ink cartridges.
3. The Complexity of Ink Production
Ink production is a complex and intricate process that involves advanced technology and precise engineering. This complexity contributes significantly to the high cost of ink cartridges.
3.1 Thermal vs. Piezoelectric Processes
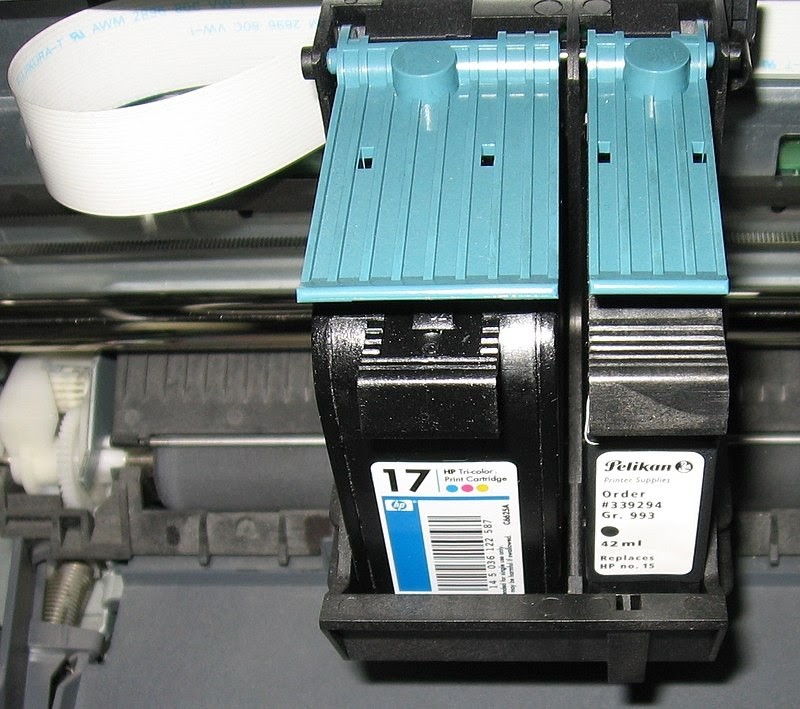
Different printer manufacturers use different printing processes. Canon, HP, and Lexmark use a thermal process where ink is heated to create bubbles that propel droplets onto the paper. Epson and Brother use a piezoelectric process, where an electrical charge changes the shape of piezoelectric material to expel ink. Both processes require sophisticated cartridge designs to prevent malfunctions.
3.2 Precision Engineering
The chambers inside printer cartridges, the filaments, and the print heads must be designed with precision to ensure consistent and reliable performance. This requires advanced engineering and manufacturing processes, adding to the cost of ink cartridges. A report by the Rochester Institute of Technology highlights the precision required in manufacturing inkjet print heads.
4. Quality and Performance
Genuine OEM ink is designed to provide the highest quality and safest option for printer owners. This commitment to quality comes at a higher price.
4.1 Superior Print Quality
OEM ink cartridges are engineered to work seamlessly with specific printer models, ensuring optimal print quality, color accuracy, and longevity. The higher price reflects the superior performance and reliability of these cartridges. Tests conducted by PCMag consistently show that OEM cartridges outperform third-party options in terms of print quality.
4.2 Risk of Using Compatible Cartridges
While compatible or remanufactured cartridges can be cheaper, they often come with risks such as lower page yields and inconsistent image quality. Using non-OEM cartridges can sometimes lead to printer malfunctions or damage, further justifying the higher cost of genuine ink.
5. Supply and Demand Dynamics
The consistently high demand for ink, coupled with minimal fluctuation, keeps the prices for OEM ink high. The widespread use of printers in homes and offices ensures a steady demand that manufacturers capitalize on.
5.1 High Demand
With the rise of home offices and remote work, the demand for domestic printers has increased, leading to a consistently high demand for ink cartridges. This sustained demand allows manufacturers to maintain higher prices without significant drops.
5.2 Minimal Fluctuation
Unlike other products that may experience seasonal or economic fluctuations in demand, the demand for printer ink remains relatively stable. This stability allows manufacturers to predict demand accurately and maintain consistent pricing strategies.
6. Specialization and Variety
The wide range of printer models and ink types requires a great deal of specialization in ink cartridge design, which increases R&D and manufacturing costs.
6.1 Printer-Specific Cartridges
Ink cartridges are not one-size-fits-all. Each printer model requires a specific type of cartridge designed to work seamlessly with its printing technology. This specialization increases the complexity and cost of manufacturing ink cartridges.
6.2 Standard vs. High-Capacity Cartridges
Most cartridges come in standard and high-capacity (XL) versions. High-capacity cartridges offer a lower cost per page but require additional manufacturing and distribution considerations. Knowing your printer model and printing needs is essential for choosing the right cartridge.
6.3 Color Cartridge Configuration
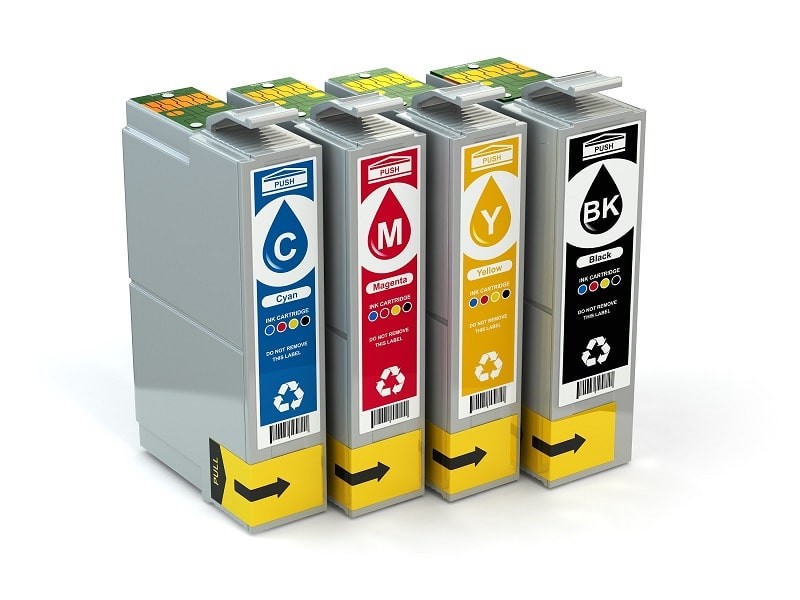
Most inkjet printers use four separate color ink cartridges: cyan (C), magenta (M), yellow (Y), and black (K). Some printers use all-in-one tri-color cartridges, which can waste ink when only one color runs out. Printers with separate color cartridges are generally more cost-effective.
7. Planned Obsolescence
Like many electronic devices, printers and their cartridges are often designed with a limited lifespan. This practice, known as planned obsolescence, ensures continued demand for replacement products.
7.1 Limited Lifespan
Printer companies can build electronics that last for decades, but doing so would reduce their profit margins. By designing printers and cartridges with a limited lifespan, manufacturers ensure that consumers will need to purchase replacements regularly.
7.2 Electronic Waste
The short lifespan of electronic devices contributes to the growing problem of electronic waste. It’s essential to properly recycle old printers and ink cartridges to minimize environmental impact. Organizations like the EPA offer guidelines on how to properly dispose of electronic waste.
8. Strategies to Extend Cartridge Life
There are several strategies you can use to extend the life of your ink and toner cartridges, reducing the frequency of replacements and saving money.
8.1 Regular Printer Use
If you don’t use your printer for long periods, the print heads can dry out. Use your printer at least once a week and perform routine maintenance (head alignment, nozzle check, etc.) once a month.
8.2 Nozzle Cleaning Techniques
If your print heads do dry out, use the printer’s built-in nozzle cleaning function to clear any clogs. You can also manually clean the print heads using a lint-free cloth and distilled water.
8.3 Print in Draft Mode
When printing documents that don’t require high quality, use draft mode or economy mode. This reduces the amount of ink used and extends the life of your cartridges.
8.4 Choose the Right Font
Certain fonts use more ink than others. Consider using lighter fonts like Century Gothic, Times New Roman, or Calibri to conserve ink.
9. Alternatives to OEM Cartridges
While OEM cartridges offer the best quality and reliability, there are alternative options that can help you save money.
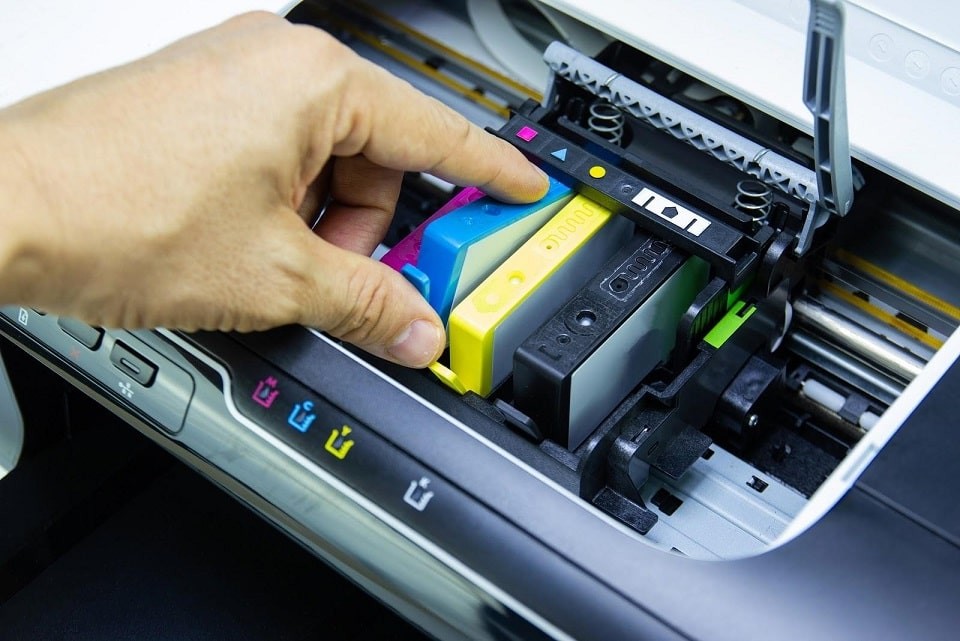
9.1 Compatible Ink Cartridges
Compatible ink cartridges are manufactured by third-party companies and are designed to work with specific printer models. They are typically cheaper than OEM cartridges but may not offer the same print quality or page yield.
9.2 Remanufactured Ink Cartridges
Remanufactured ink cartridges are OEM cartridges that have been used, cleaned, refilled, and tested. They are a more environmentally friendly option than buying new cartridges and can be cheaper than OEM cartridges. However, their reliability can vary.
9.3 Refilling Ink Cartridges
Refilling ink cartridges involves purchasing ink and refilling the cartridges yourself. While this can be the cheapest option, it can also be messy and awkward. Refilled cartridges may not perform as well as OEM or remanufactured cartridges.
10. Optimizing Your Printing Habits
Changing your printing habits can significantly reduce your ink consumption and save money in the long run.
10.1 Preview Before Printing
Always preview your documents before printing to avoid printing unnecessary pages or errors.
10.2 Print Only What You Need
Avoid printing entire documents when only specific pages are needed. Use the print range option to print only the necessary pages.
10.3 Digital Alternatives
Whenever possible, use digital alternatives instead of printing. Share documents electronically, take notes on a tablet, and store files in the cloud.
10.4 Print on Both Sides
Enable duplex printing to print on both sides of the paper. This reduces paper consumption and can also save on ink costs.
11. Ink Subscription Services
Many printer manufacturers offer ink subscription services that automatically ship replacement ink cartridges to your door when your printer detects low ink levels.
11.1 Convenience and Cost Savings
Ink subscription services can be convenient and cost-effective for users who print frequently. These services typically offer discounted ink prices and free shipping.
11.2 Potential Drawbacks
However, ink subscription services may not be suitable for everyone. Some users have reported issues with costly automated refills and difficulty unsubscribing from the services.
12. The Cost of Toner Cartridges
Toner cartridges, used in laser printers, are also expensive for many of the same reasons as ink cartridges.
12.1 Similar Factors
The high cost of toner cartridges can be attributed to factors such as supply and demand, research and development, specialization, and pricing strategies.
12.2 Cost Per Page
Toner cartridges typically offer a better cost per page compared to ink cartridges. Laser printers are more efficient for high-volume printing.
13. Finding Affordable Ink and Toner
Despite the high cost of ink and toner cartridges, there are ways to find affordable options.
13.1 Shop Around
Compare prices from different retailers to find the best deals on genuine, brand-name ink and toner cartridges.
13.2 Online Retailers
Online retailers often offer better prices than brick-and-mortar stores. Look for discounts, coupons, and free shipping offers.
13.3 Wholesale Options
If you need a large quantity of ink or toner cartridges, consider buying in bulk or exploring wholesale options.
14. The Environmental Impact of Ink Cartridges
The production and disposal of ink cartridges have a significant environmental impact.
14.1 Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of ink cartridges requires energy, water, and raw materials. It also generates waste and pollution.
14.2 Landfill Waste
Millions of ink cartridges end up in landfills each year, where they can take hundreds of years to decompose.
14.3 Recycling Options
Recycling ink cartridges can help reduce their environmental impact. Many retailers and manufacturers offer recycling programs.
15. Innovations in Printing Technology
Innovations in printing technology are aimed at reducing ink consumption and lowering printing costs.
15.1 Inkjet Alternatives
Manufacturers are developing inkjet alternatives that use less ink and offer better efficiency.
15.2 Tank Printers
Tank printers use refillable ink tanks instead of cartridges. This can significantly reduce ink costs over time.
15.3 Solid Ink Printers
Solid ink printers use solid blocks of ink instead of liquid ink. This technology produces less waste and offers vibrant colors.
16. Addressing the High Cost of Ink
The high cost of ink cartridges is a complex issue with no easy solutions. However, consumers can take steps to minimize their ink consumption, explore alternative options, and support sustainable practices.
16.1 Consumer Awareness
Increased consumer awareness about the factors driving up ink prices can help drive demand for more affordable and sustainable solutions.
16.2 Industry Pressure
Pressure from consumers and environmental groups can encourage manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices and offer more affordable ink options.
16.3 Regulatory Measures
Government regulations can help address issues such as planned obsolescence and promote the recycling of electronic waste.
17. The Future of Printing
The future of printing is likely to involve more sustainable practices, innovative technologies, and affordable ink options.
17.1 Sustainable Solutions
Manufacturers are increasingly focused on developing sustainable printing solutions that minimize environmental impact.
17.2 Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are expected to lead to more efficient printers and lower ink consumption.
17.3 Affordable Options
Competition and consumer demand will likely drive the development of more affordable ink options.
18. Expert Opinions on Ink Costs
Experts in the printing industry offer insights into the reasons behind high ink costs and potential solutions.
18.1 Industry Analysts
Industry analysts point to the razor and blades business model as the primary driver of high ink prices.
18.2 Environmental Advocates
Environmental advocates emphasize the need for more sustainable printing practices and greater recycling efforts.
18.3 Consumer Advocates
Consumer advocates call for greater transparency in ink pricing and encourage consumers to explore alternative options.
19. Case Studies: Comparing Ink Costs
Examining case studies can provide a clearer understanding of the true cost of printing with different printers and ink options.
19.1 Home vs. Office Printers
Home printers typically have higher ink costs per page compared to office printers.
19.2 Inkjet vs. Laser Printers
Inkjet printers are generally cheaper to buy but have higher ink costs, while laser printers are more expensive upfront but offer lower toner costs per page.
19.3 OEM vs. Compatible Cartridges
Using compatible cartridges can save money but may result in lower print quality and higher risk of printer malfunctions.
20. Resources for Finding Affordable Ink
There are numerous resources available to help consumers find affordable ink and toner cartridges.
20.1 Online Retailers
Websites like Amazon, eBay, and Toner Buzz offer a wide selection of ink and toner cartridges at competitive prices.
20.2 Coupon Websites
Websites like RetailMeNot and Coupons.com offer discounts and coupon codes for ink and toner purchases.
20.3 Local Retailers
Local office supply stores and electronics retailers may offer competitive prices and special promotions.
In conclusion, the high cost of ink cartridges is a multifaceted issue influenced by business models, research and development costs, and supply and demand dynamics. By understanding these factors and adopting smart printing habits, consumers can minimize their ink consumption and save money.
Do you have more questions about printer ink costs? Visit WHY.EDU.VN, located at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101, to get answers from our experts. We are dedicated to providing accurate and reliable information to help you make informed decisions. Let why.edu.vn be your go-to resource for all your questions.
FAQ: Understanding Ink Cartridge Costs
Here are some frequently asked questions about why ink cartridges are so expensive, covering areas like ink volume, pricing, and alternative options:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. Why is printer ink so expensive? | The high cost is due to the razor and blades business model, R&D investments, complex production, demand, and planned obsolescence. |
| 2. Is it cheaper to buy a new printer? | Not usually. Printers are often sold at a loss to make money on ink sales. |
| 3. Are OEM cartridges worth the cost? | OEM cartridges offer superior quality and reliability but come at a higher price. |
| 4. Can I use compatible cartridges? | Yes, but they may not offer the same print quality or reliability as OEM cartridges. |
| 5. How can I extend ink cartridge life? | Use draft mode, print less frequently, and perform regular printer maintenance. |
| 6. What is an ink subscription service? | An automatic refill program that ships replacement cartridges to your door when your printer detects low ink levels. |
| 7. Why are toner cartridges expensive too? | Toner cartridges share similar factors: supply and demand, research and development, specialization, and pricing strategies. |
| 8. What is the environmental impact? | Ink cartridges contribute to landfill waste and require resources to manufacture, making recycling crucial. |
| 9. Are there innovations in printing? | Yes, innovations like tank printers and solid ink printers aim to reduce ink consumption and lower costs. |
| 10. How to find affordable ink options? | Shop around, look for online retailers, use coupons, and consider wholesale options. |







This detailed analysis should provide a comprehensive understanding of why ink cartridges are so expensive, the various factors involved, and potential solutions for consumers looking to save money.