Why Am I Always Coughing? Discover the common causes of persistent coughs and explore effective relief strategies with insights from WHY.EDU.VN. Addressing everything from postnasal drip to asthma, find out how to manage your chronic cough and improve your quality of life. Learn about the various factors contributing to a continuous cough, remedies, and when to seek expert advice to breathe easier. This guide includes information about cough triggers and respiratory health.
1. Understanding the Nature of Coughing
Coughing, although often viewed negatively, is a crucial defense mechanism. It helps clear your airways of irritants, mucus, and foreign particles, protecting your lungs from infection. This natural reflex, whether voluntary or involuntary, is triggered by nerve stimulation in your larynx and respiratory tract, as explained by respiratory specialists at WHY.EDU.VN.
Understanding the mechanics and triggers of coughing can aid in identifying and addressing underlying causes, which is why we’ve compiled this comprehensive guide.
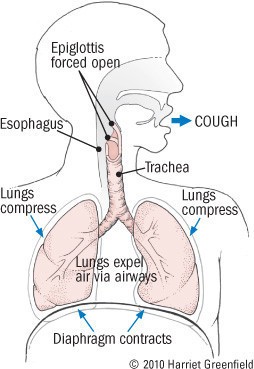
Anatomy of a Cough
Coughing involves several coordinated steps:
- Inhalation: A deep breath fills the lungs with air.
- Glottis Closure: The glottis (the opening between the vocal cords) closes, sealing the trachea.
- Muscle Contraction: Chest, abdominal, and diaphragm muscles contract forcefully, increasing pressure in the airways.
- Glottis Opening: The glottis suddenly opens, releasing a high-speed burst of air.
This process helps expel irritants and protect the respiratory system.
2. Defining the Chronic Cough
While occasional coughing is normal, a cough is considered chronic if it persists for more than eight weeks. This prolonged coughing can stem from various underlying issues and significantly impact your life. Understanding what differentiates an acute cough from a chronic one is essential for seeking appropriate care.
Chronic coughing can be disruptive and uncomfortable. It can lead to fatigue, sleep disturbances, and even physical complications like urinary incontinence or rib fractures. It’s important to identify the underlying cause and seek effective treatment.
3. Common Causes of Chronic Coughing
Chronic coughing can arise from various underlying conditions. Identifying these potential causes is crucial for determining the most effective treatment strategy.
- Postnasal Drip
- Asthma
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Chronic Bronchitis
- ACE Inhibitors
4. Postnasal Drip (Upper Airway Cough Syndrome)
Postnasal drip is a common culprit behind chronic coughing. This condition occurs when excess mucus drips down the back of your throat, irritating the nerves and triggering a cough.
Your nose naturally produces mucus to keep the nasal passages moist and trap debris. However, conditions like allergies, colds, or sinus infections can cause increased mucus production, leading to postnasal drip. This excess mucus irritates the throat and triggers the cough reflex.
4.1. Symptoms of Postnasal Drip
Common symptoms include:
- Frequent throat clearing
- A sensation of mucus dripping down the throat
- Sore throat
- Coughing, particularly at night
4.2. Managing Postnasal Drip
Effective management strategies include:
- Decongestants and Antihistamines: Over-the-counter medications can help reduce mucus production and clear nasal passages. Always follow the directions and be aware of potential side effects.
- Nasal Irrigation: Use a saline nasal spray or a neti pot to rinse nasal passages and remove excess mucus. This can help alleviate irritation and reduce coughing.
- Steam Inhalation: Inhaling steam from a hot shower or a bowl of hot water can help loosen mucus and soothe irritated airways.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to keep mucus thin and easier to clear.
5. Asthma and Cough-Variant Asthma
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. While wheezing and shortness of breath are common symptoms, some individuals experience coughing as their primary symptom, known as cough-variant asthma (CVA).
5.1. Understanding Cough-Variant Asthma
CVA is a type of asthma where the main symptom is a persistent, dry cough. Unlike typical asthma, wheezing may be minimal or absent. The cough is often triggered by factors such as allergens, irritants, exercise, or cold air.
5.2. Diagnosing Asthma
Diagnosing asthma involves several steps:
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): These tests measure lung capacity and airflow.
- Methacholine Challenge Test: This test involves inhaling a substance that can trigger airway narrowing in people with asthma.
- Trial Treatment: If asthma is suspected, a trial of asthma medications may be prescribed to see if the cough improves.
5.3. Managing Asthma and CVA
Effective management strategies include:
- Inhaled Corticosteroids: These medications reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Bronchodilators: These medications help open up the airways, making it easier to breathe.
- Trigger Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding triggers such as allergens, irritants, and cold air can help reduce coughing.
6. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD is a condition where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation. While heartburn is a common symptom, GERD can also cause coughing, even without the presence of heartburn.
6.1. How GERD Triggers Coughing
When stomach acid enters the esophagus, it can irritate nerve endings, triggering the cough reflex. This can occur even if you don’t experience heartburn or other typical GERD symptoms.
6.2. Symptoms of GERD-Related Cough
Common symptoms include:
- Chronic cough, particularly at night
- Hoarseness
- Sore throat
- A sensation of a lump in the throat
6.3. Managing GERD-Related Cough
Effective management strategies include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoid foods and beverages that trigger GERD, such as caffeine, alcohol, chocolate, and spicy foods. Eat smaller meals and avoid lying down for at least two to three hours after eating.
- Antacids: Over-the-counter antacids can help neutralize stomach acid and provide temporary relief.
- H2 Blockers and Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): These medications reduce stomach acid production. Stronger versions are available by prescription.
- Elevating the Head of the Bed: Raising the head of the bed can help prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus during sleep.
7. Chronic Bronchitis and Bronchiectasis
Chronic bronchitis and bronchiectasis are both chronic respiratory conditions characterized by inflammation and damage to the airways.
7.1. Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis involves long-term inflammation of the bronchial tubes, leading to airway narrowing and increased mucus production. It’s often caused by smoking or long-term exposure to air pollutants.
7.2. Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a condition where the walls of the bronchial tubes are damaged, leading to chronic inflammation and increased susceptibility to infections.
7.3. Symptoms of Chronic Bronchitis and Bronchiectasis
Common symptoms include:
- Chronic cough, often producing mucus
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Frequent respiratory infections
7.4. Managing Chronic Bronchitis and Bronchiectasis
Effective management strategies include:
- Quitting Smoking: If you smoke, quitting is the most important step in managing chronic bronchitis.
- Avoiding Air Pollutants: Minimize exposure to air pollutants and irritants.
- Bronchodilators: These medications help open up the airways, making it easier to breathe.
- Corticosteroids: Inhaled corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat respiratory infections.
8. ACE Inhibitors and Coughing
ACE inhibitors are medications commonly used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. A common side effect of ACE inhibitors is a persistent, dry cough.
8.1. How ACE Inhibitors Trigger Coughing
ACE inhibitors can increase levels of bradykinin, a substance that can irritate the airways and trigger coughing.
8.2. Managing ACE Inhibitor-Related Cough
The primary way to manage this cough is to switch to another type of medication, such as an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB). ARBs work similarly to ACE inhibitors but are less likely to cause coughing.
9. Less Common Causes of Persistent Coughing
While the conditions mentioned above are the most common causes of chronic coughing, other potential causes include:
- Lung Infections: Infections like pneumonia, tuberculosis, and fungal infections can cause a persistent cough.
- Pertussis (Whooping Cough): This highly contagious respiratory infection can cause severe coughing fits.
- Heart Disease: Heart failure can cause coughing and shortness of breath.
- Aspiration: When food or liquids enter the airways instead of the esophagus, it can lead to coughing.
- Environmental Irritants: Exposure to pollutants, smoke, dust, and other irritants can trigger coughing.
- Lung Cancer: While less common in non-smokers, lung cancer can cause a persistent cough.
- Stress: Psychological factors can contribute to coughing in some individuals.
10. When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of chronic coughing can be managed with over-the-counter remedies and lifestyle modifications, it’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Fever
- Coughing up blood
- Shortness of breath
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
- Chest pain
- Wheezing
These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires prompt medical evaluation and treatment.
11. Exploring Cough Remedies and Relief
When dealing with a persistent cough, various remedies can provide relief. These include over-the-counter options, home remedies, and prescription medications.
11.1. Over-the-Counter Medications
- Expectorants: These medications, such as guaifenesin, help loosen mucus, making it easier to cough up.
- Cough Suppressants: These medications, such as dextromethorphan, can help suppress the cough reflex.
- Decongestants: These medications help clear nasal passages and reduce postnasal drip.
- Antihistamines: These medications help reduce allergy symptoms that can contribute to coughing.
11.2. Home Remedies
- Honey: Honey has been shown to be effective in soothing coughs, particularly in children.
- Warm Liquids: Drinking warm liquids such as tea, broth, or lemon water can help soothe the throat and loosen mucus.
- Humidifier: Using a humidifier can help add moisture to the air, which can soothe irritated airways.
- Salt Water Gargle: Gargling with warm salt water can help soothe a sore throat and reduce inflammation.
11.3. Prescription Medications
If over-the-counter remedies and home remedies are not effective, your doctor may prescribe medications such as:
- Inhaled Corticosteroids: These medications reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Bronchodilators: These medications help open up the airways, making it easier to breathe.
- Antibiotics: If your cough is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed.
12. Understanding Diagnostic Processes
When a chronic cough persists, understanding the diagnostic procedures can alleviate anxiety and ensure appropriate care. Doctors employ various methods to pinpoint the exact cause and tailor effective treatments.
Diagnostic procedures often include physical exams, reviewing medical history, and specific tests to evaluate the respiratory system. These processes ensure that underlying issues are identified accurately and addressed effectively.
12.1. Initial Assessment and Physical Exam
The first step usually involves a detailed discussion of your medical history and a thorough physical examination. This assessment helps the doctor understand your symptoms, potential risk factors, and overall health.
12.2. Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as chest X-rays or CT scans, may be used to visualize the lungs and airways. These tests can help identify structural abnormalities, infections, or other potential causes of coughing.
12.3. Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs)
Pulmonary function tests measure how well your lungs are working. These tests can help diagnose asthma, chronic bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions.
12.4. Bronchoscopy
In some cases, a bronchoscopy may be performed. This procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera into your airways to visualize them and collect samples for further testing.
13. Lifestyle Adjustments for Managing Coughs
Making specific lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of chronic coughs. These adjustments, combined with medical treatments, can improve overall respiratory health.
Adjustments such as avoiding triggers, staying hydrated, and maintaining a healthy diet can play a vital role in managing coughs. Incorporating these habits can lead to long-term relief and better quality of life.
13.1. Avoiding Irritants
Minimizing exposure to irritants such as smoke, pollutants, and allergens can help reduce coughing. This includes avoiding smoking, using air purifiers, and keeping your environment clean.
13.2. Staying Hydrated
Drinking plenty of fluids helps keep mucus thin and easier to clear, reducing the urge to cough. Water, herbal teas, and clear broths are excellent choices.
13.3. Maintaining a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health and can strengthen your immune system. Avoiding foods that trigger acid reflux can also reduce coughing related to GERD.
14. The Role of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors significantly influence the prevalence and intensity of chronic coughs. Understanding these factors can help in making informed decisions to protect your respiratory health.
Factors such as air quality, climate, and occupational hazards play a critical role in respiratory health. Awareness and proactive measures can mitigate the impact of these environmental factors.
14.1. Air Quality
Poor air quality, including pollutants and allergens, can exacerbate coughing. Monitoring air quality reports and taking precautions on high-pollution days is advisable.
14.2. Climate Conditions
Extreme temperatures and dry air can irritate the airways. Using humidifiers in dry climates and avoiding prolonged exposure to cold air can help.
14.3. Occupational Hazards
Certain occupations involve exposure to irritants and pollutants that can cause chronic coughing. Proper protective equipment and ventilation can minimize these risks.
15. Navigating Social and Psychological Impacts
Chronic coughing extends beyond physical discomfort, affecting social interactions and psychological well-being. Addressing these impacts is crucial for overall quality of life.
Social isolation and anxiety are common among individuals with chronic coughs. Recognizing these effects and seeking appropriate support can lead to improved mental health and social engagement.
15.1. Social Isolation
Frequent coughing can lead to embarrassment and social withdrawal. Communicating with others about your condition and seeking support can help maintain social connections.
15.2. Anxiety and Stress
The uncertainty and disruption caused by chronic coughing can lead to anxiety and stress. Relaxation techniques, counseling, and support groups can provide valuable coping strategies.
15.3. Impact on Sleep
Coughing at night can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue and reduced quality of life. Strategies such as elevating the head of the bed and using a humidifier can improve sleep quality.
16. Advances in Cough Research
Ongoing research continues to uncover new insights into the causes and treatments of chronic coughs. Staying informed about these advancements can empower you to make the best decisions for your health.
Recent studies have led to the development of novel therapies and diagnostic techniques. Engaging with these advancements can provide hope and new avenues for managing chronic coughs effectively.
16.1. Novel Therapies
Researchers are exploring new medications and therapies targeting specific cough mechanisms. These include drugs that reduce airway inflammation and block cough receptors.
16.2. Diagnostic Techniques
Advanced diagnostic tools, such as high-resolution imaging and molecular testing, are improving the accuracy and speed of cough diagnosis.
17. Expert Insights from WHY.EDU.VN
WHY.EDU.VN is committed to providing comprehensive and reliable health information. Our team of experts offers insights into managing chronic coughs and improving respiratory health.
At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of living with a chronic cough. Our resources are designed to provide you with the knowledge and support you need to breathe easier and live better.
18. Seeking Expert Advice
If you’re struggling with a persistent cough, don’t hesitate to seek expert advice from healthcare professionals. A proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan can make a significant difference in your quality of life.
The information provided in this guide is intended for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult with a healthcare provider to address your specific health concerns.
Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (213) 555-0101
Website: WHY.EDU.VN
FAQ: Common Questions About Chronic Coughs
Q1: What is considered a chronic cough?
A chronic cough is defined as a cough that lasts for eight weeks or longer.
Q2: What are the most common causes of chronic cough?
The most common causes include postnasal drip, asthma, GERD, chronic bronchitis, and ACE inhibitors.
Q3: How can I tell if my cough is due to postnasal drip?
Symptoms of postnasal drip include frequent throat clearing, a sensation of mucus dripping down the throat, and coughing, particularly at night.
Q4: Can asthma cause coughing without wheezing?
Yes, cough-variant asthma is a type of asthma where the primary symptom is a persistent, dry cough without wheezing.
Q5: How can GERD cause coughing?
Stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus can irritate nerve endings, triggering the cough reflex, even without heartburn.
Q6: What lifestyle changes can help manage chronic cough?
Lifestyle changes include avoiding irritants, staying hydrated, maintaining a healthy diet, and elevating the head of the bed.
Q7: When should I see a doctor for a chronic cough?
You should see a doctor if you experience fever, coughing up blood, shortness of breath, weight loss, night sweats, or chest pain.
Q8: What is the role of environmental factors in chronic cough?
Environmental factors such as air quality, climate, and occupational hazards can exacerbate coughing.
Q9: How can I manage the social and psychological impacts of chronic cough?
Managing social and psychological impacts involves communicating with others, seeking support, practicing relaxation techniques, and improving sleep quality.
Q10: Are there new advances in cough research?
Yes, ongoing research is uncovering novel therapies and diagnostic techniques for chronic coughs.
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth understanding of chronic coughs, their causes, and effective management strategies. At why.edu.vn, we are dedicated to helping you find the answers and support you need to live a healthier, more comfortable life. Visit our website or contact us today for more information and expert assistance.