Abortion should stay legal because it is a fundamental right that protects reproductive freedom, ensures women’s health, and supports individual autonomy. At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities surrounding this critical issue. Explore how safeguarding access to abortion promotes gender equality, reduces unsafe practices, and upholds the principles of bodily autonomy.
1. The Foundational Right to Bodily Autonomy
Bodily autonomy is the principle that each person has the right to control their own body and make decisions about their healthcare. This principle is fundamental to individual liberty and is a cornerstone of medical ethics.
1.1. The Significance of Bodily Autonomy
Bodily autonomy allows individuals to make informed decisions about their health, including reproductive choices. Denying this right infringes upon personal freedom and self-determination. According to the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU), “The decision whether to have a child is central to a person’s life, health, and well-being.”
1.2. How Legal Abortion Upholds Bodily Autonomy
Legal abortion ensures that individuals can make autonomous decisions about their reproductive health without government interference. When abortion is legal, people have the freedom to decide whether to continue a pregnancy based on their personal circumstances, values, and beliefs.
2. Protecting Women’s Health and Well-being
Legalizing abortion is essential for safeguarding the health and well-being of women, particularly those facing medical complications or difficult life circumstances.
2.1. Reducing Unsafe Abortions
When abortion is illegal, it does not stop; it merely drives the procedure underground, leading to unsafe practices. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that approximately 25 million unsafe abortions occur each year, resulting in significant health complications and fatalities. Legalizing abortion ensures that procedures are performed by trained medical professionals in safe environments, significantly reducing the risk of complications.
2.2. Addressing Medical Necessity
In some cases, abortion is necessary to protect a woman’s health or save her life. Conditions such as ectopic pregnancies, severe pre-eclampsia, or other life-threatening conditions may require abortion as a medical intervention. Restricting access to abortion in these situations can have devastating consequences.
2.3. Supporting Mental Health
Unwanted pregnancies can have profound effects on a woman’s mental health. For some, carrying an unwanted pregnancy to term can lead to depression, anxiety, and other psychological distress. Legal abortion provides an option for women to avoid these potential mental health challenges.
3. Socioeconomic Factors and Reproductive Choice
Access to legal abortion is closely linked to socioeconomic factors. Restricting abortion disproportionately affects marginalized communities and perpetuates cycles of poverty.
3.1. Economic Impact on Families
Raising a child incurs significant financial costs, including expenses for healthcare, education, and daily necessities. For individuals and families already struggling financially, an unplanned pregnancy can exacerbate economic hardship. Legal abortion allows individuals to make choices that align with their financial capabilities and reduce the risk of economic instability.
3.2. Educational and Career Opportunities
Unplanned pregnancies can interrupt educational and career goals, particularly for young women. Access to legal abortion enables individuals to pursue their education and career aspirations without the burden of unintended parenthood.
3.3. Impact on Child Welfare
Children born into unwanted or unsupported environments may face poorer outcomes in terms of health, education, and overall well-being. By allowing individuals to choose when and whether to have children, legal abortion can contribute to improved child welfare.
4. Addressing Cases of Rape and Incest
In cases of rape and incest, forcing a survivor to carry a pregnancy to term can be deeply traumatic and re-victimizing. Legal abortion provides a compassionate option for survivors to terminate pregnancies resulting from these violent acts.
4.1. The Trauma of Forced Pregnancy
Carrying a pregnancy resulting from rape or incest can cause severe psychological distress, triggering memories of the assault and compounding the trauma experienced by the survivor. Legal abortion allows survivors to regain control over their bodies and avoid the emotional pain of carrying an unwanted pregnancy.
4.2. Justice and Healing
For many survivors, access to abortion is an essential component of the healing process. It allows them to make a choice that aligns with their emotional needs and supports their journey toward recovery.
5. The Role of Personal Beliefs and Values
Respecting individual beliefs and values is crucial in a diverse society. Legalizing abortion allows individuals to make decisions that align with their personal moral and ethical frameworks.
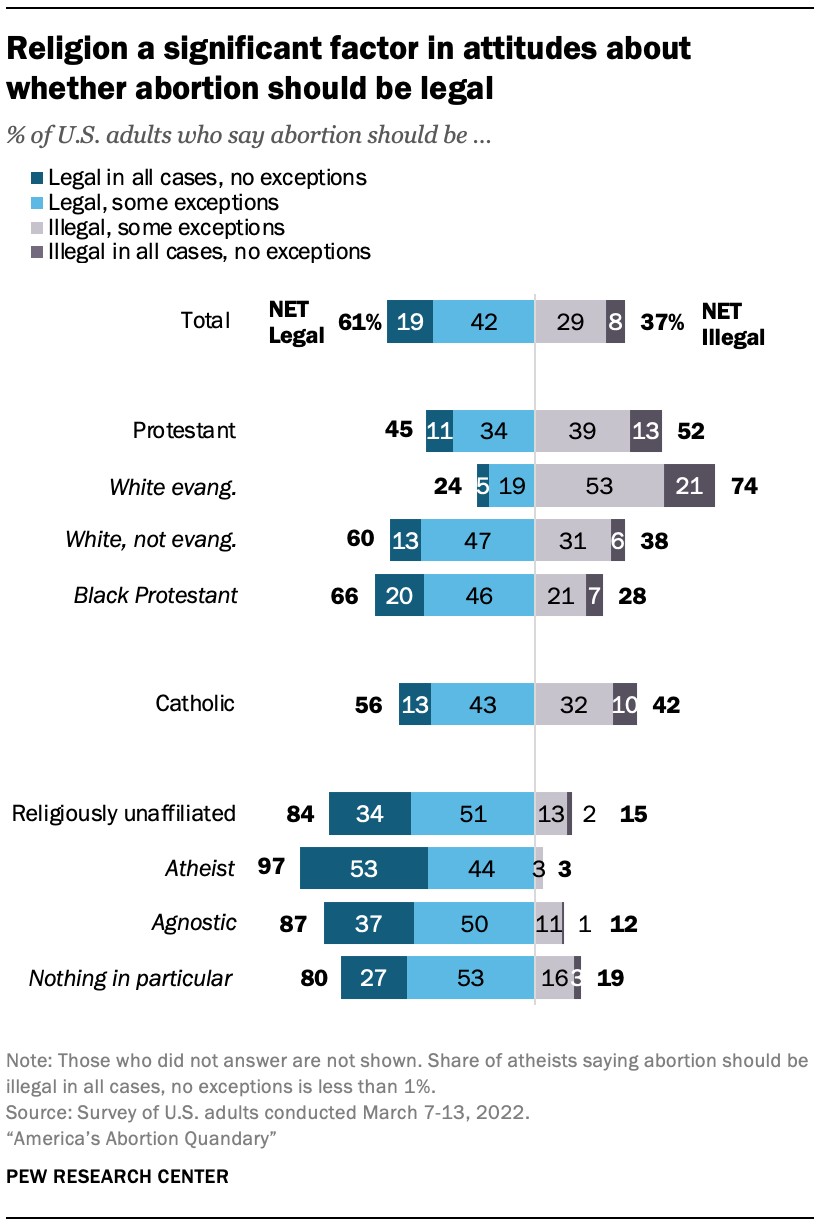
5.1. Religious Freedom
Religious beliefs about abortion vary widely. While some religious traditions oppose abortion in all circumstances, others support the right to choose. Legal abortion respects religious freedom by allowing individuals to make decisions consistent with their own faith or conscience.
5.2. Moral Autonomy
Moral autonomy is the principle that individuals should have the freedom to make their own moral judgments and decisions. Legal abortion upholds moral autonomy by allowing people to make decisions about reproductive health based on their personal values and ethical considerations.
6. International Human Rights Standards
International human rights law recognizes the right to reproductive health, including access to safe and legal abortion.
6.1. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights affirms the right to life, liberty, and security of person. Denying access to safe and legal abortion can violate these rights by endangering a woman’s health and well-being.
6.2. International Treaties and Conventions
Several international treaties and conventions recognize the importance of reproductive rights, including the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW). These agreements call on states to ensure access to reproductive healthcare services, including abortion.
7. Public Opinion and Abortion Access
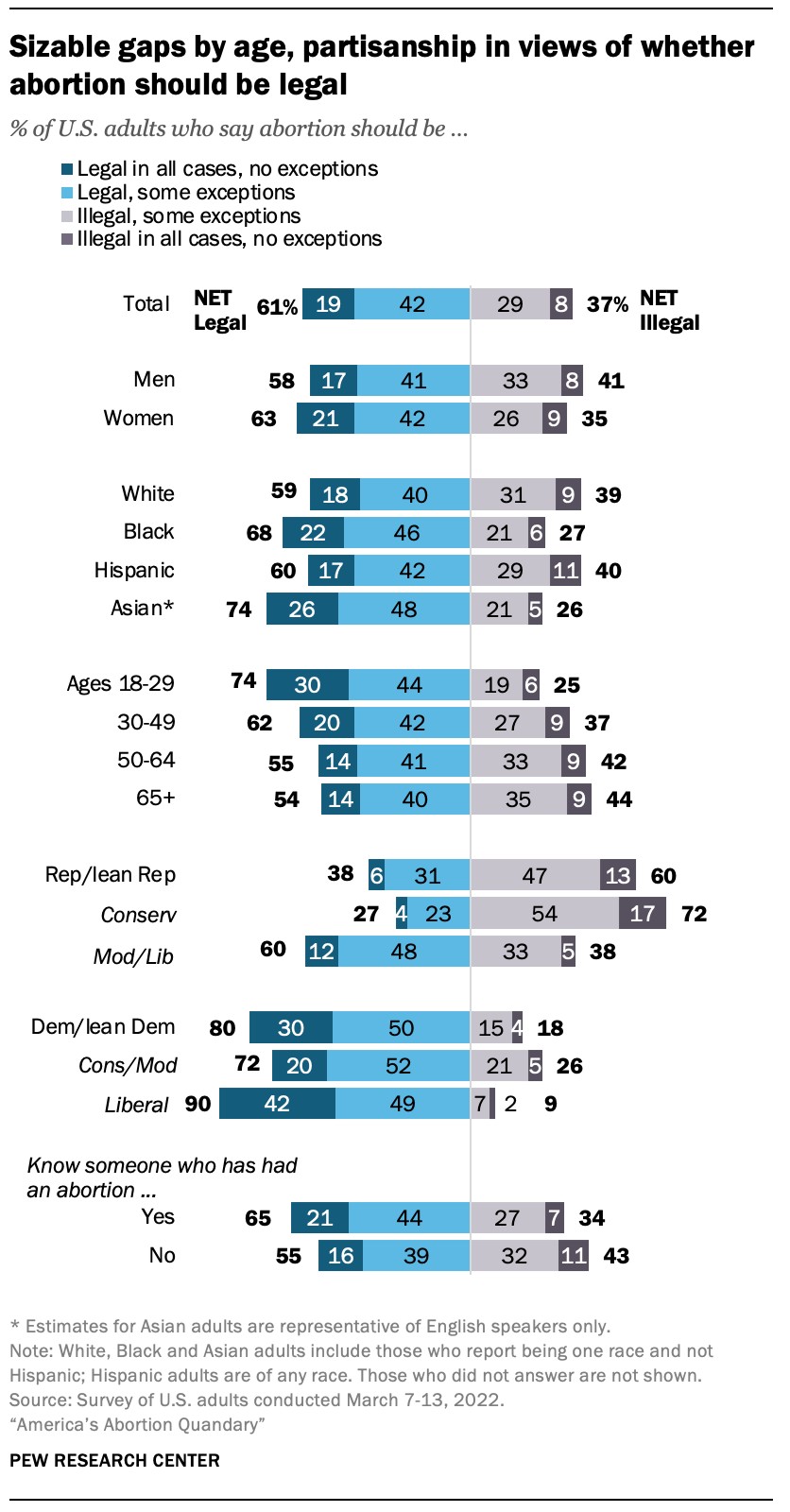
Public opinion in the United States generally supports access to abortion, particularly in certain circumstances. Understanding public sentiment is crucial for informed policy-making.
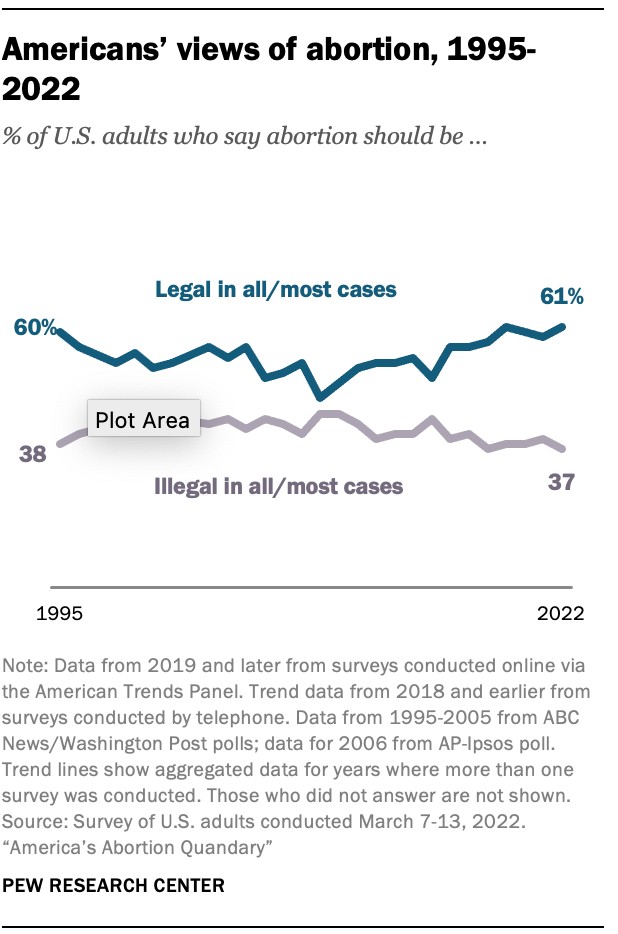
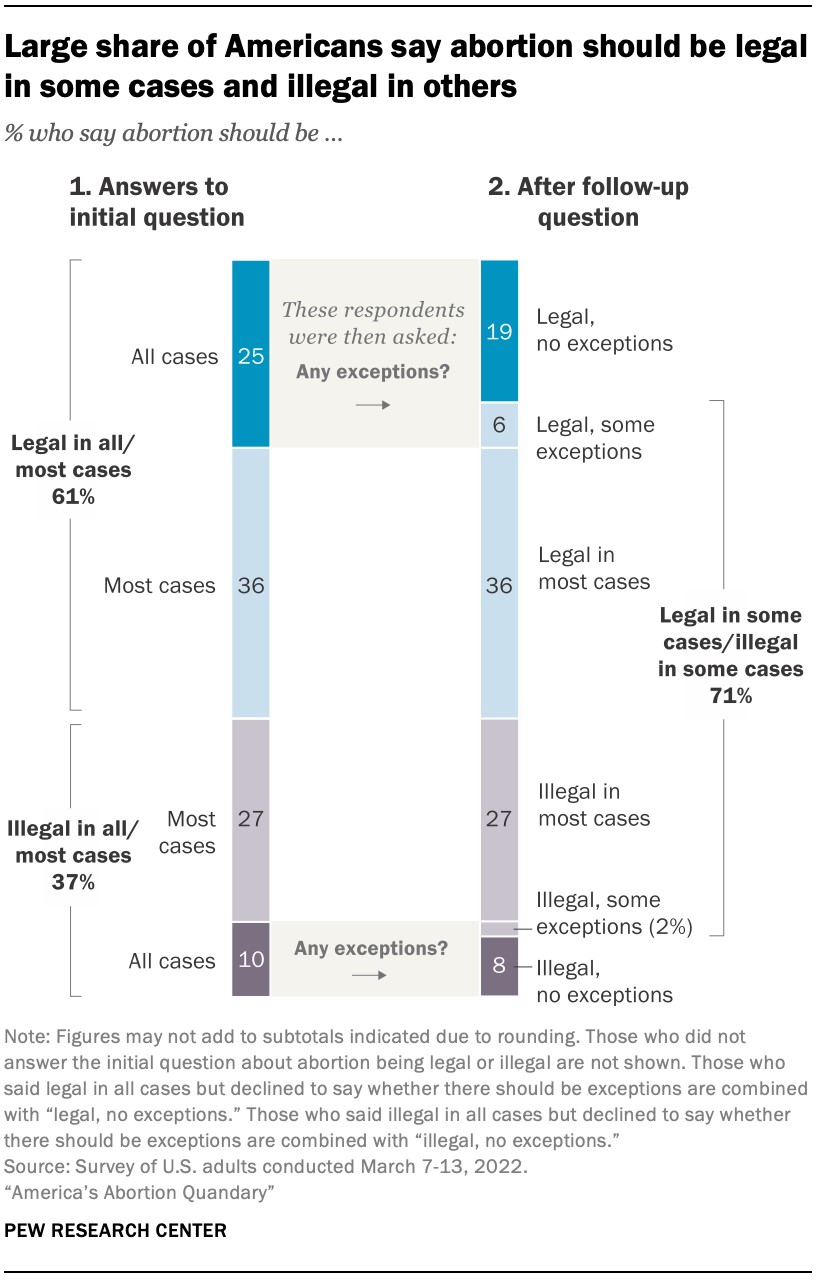
7.1. Majority Support for Legal Abortion
Recent polls indicate that a majority of Americans believe abortion should be legal in all or most cases. According to a Pew Research Center study, approximately 61% of U.S. adults support legal abortion.
7.2. Nuances in Public Opinion
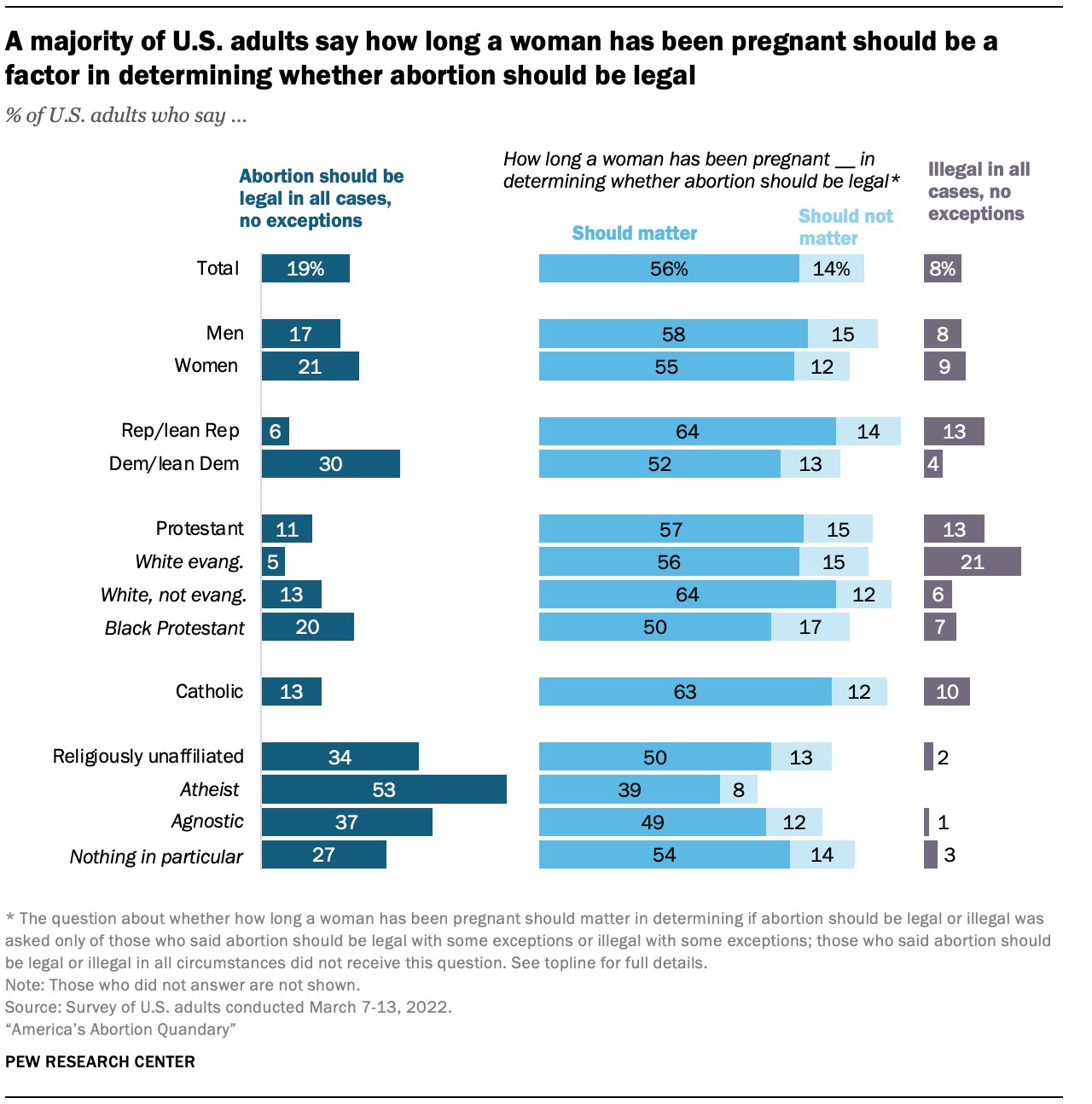
Public opinion on abortion can vary depending on the circumstances and stage of pregnancy. While many support abortion early in pregnancy, support tends to decrease as the pregnancy progresses.
8. The Impact of Restricting Abortion Access
Restricting access to abortion has far-reaching consequences for individuals, families, and communities.
8.1. Increased Maternal Mortality
Studies have shown that restricting abortion access can lead to an increase in maternal mortality rates. When safe, legal abortion is not available, more women may resort to unsafe practices, leading to complications and death.
8.2. Disproportionate Impact on Marginalized Groups
Restrictions on abortion disproportionately affect low-income individuals, women of color, and those living in rural areas. These groups often face barriers to accessing healthcare services, and limiting abortion access exacerbates these inequalities.
8.3. Strain on Social Services
When abortion is restricted, more unintended pregnancies may result in births, placing additional strain on social services such as welfare programs, childcare support, and adoption services.
9. Fetal Viability and Abortion Laws
Fetal viability, the point at which a fetus can survive outside the womb, is often a central consideration in debates about abortion laws.
9.1. Defining Fetal Viability
Fetal viability typically occurs around 24 weeks of gestation, although this can vary depending on medical advancements and individual circumstances. Abortion laws often place restrictions on abortions performed after the point of viability.
9.2. Medical Advancements and Viability
Advances in medical technology have led to improvements in the survival rates of premature infants. However, even with the best medical care, infants born before 24 weeks face significant health risks and may not survive.
10. Alternatives to Abortion
Exploring alternatives to abortion, such as adoption and comprehensive sex education, is important for providing individuals with a range of options.
10.1. Adoption
Adoption is a loving alternative to abortion that allows individuals to provide a child with a permanent home. However, adoption is not the right choice for everyone, and it should not be presented as a replacement for abortion access.
10.2. Comprehensive Sex Education
Comprehensive sex education can help reduce unintended pregnancies by providing individuals with the knowledge and skills to make informed decisions about their sexual health. This includes information about contraception, safe sex practices, and healthy relationships.
11. The Role of Empathy and Compassion
Approaching the issue of abortion with empathy and compassion is essential for fostering constructive dialogue and finding common ground.
11.1. Understanding Different Perspectives
People hold diverse views on abortion based on their personal experiences, values, and beliefs. Listening to and understanding these different perspectives is crucial for fostering empathy and respect.
11.2. Supporting Individuals in Need
Providing support and resources to individuals facing difficult reproductive choices is an act of compassion. This includes access to healthcare, counseling, and other services that can help them make informed decisions.
12. How Does Socioeconomic Status Affect Abortion Access?
Socioeconomic status significantly affects abortion access, creating disparities that impact marginalized communities.
12.1. Financial Barriers
Low-income individuals often face financial barriers to accessing abortion services, including the cost of the procedure, transportation, and accommodation.
12.2. Geographic Disparities
People living in rural areas may have limited access to abortion providers, requiring them to travel long distances and incur additional expenses.
12.3. Policy Restrictions
Policies such as mandatory waiting periods and parental consent laws can create additional barriers to abortion access, particularly for low-income individuals and young people.
13. Legal Precedents and the Right to Abortion
Legal precedents, such as Roe v. Wade, have played a significant role in establishing and protecting the right to abortion in the United States.
13.1. Roe v. Wade
Roe v. Wade (1973) was a landmark Supreme Court decision that recognized a woman’s constitutional right to abortion, based on the right to privacy.
13.2. Planned Parenthood v. Casey
Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992) affirmed the central holding of Roe v. Wade but introduced the “undue burden” standard, which allows states to regulate abortion as long as the regulations do not create a substantial obstacle to a woman seeking an abortion.
13.3. Current Legal Challenges
The right to abortion continues to face legal challenges in the United States, with many states enacting laws that restrict access to abortion services.
14. The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a critical role in providing abortion services and counseling to individuals facing reproductive choices.
14.1. Providing Comprehensive Care
Healthcare providers should offer comprehensive reproductive healthcare services, including contraception, prenatal care, and abortion services, to meet the diverse needs of their patients.
14.2. Counseling and Support
Healthcare providers should offer unbiased counseling and support to individuals facing reproductive choices, ensuring that they have the information and resources they need to make informed decisions.
14.3. Protecting Patient Privacy
Healthcare providers have a responsibility to protect patient privacy and confidentiality, ensuring that individuals feel safe and supported when seeking reproductive healthcare services.
15. Addressing Common Misconceptions about Abortion
Addressing common misconceptions about abortion is important for promoting informed dialogue and understanding.
15.1. Abortion and Mental Health
Contrary to some claims, studies have shown that abortion does not typically lead to long-term mental health problems. In fact, many individuals experience relief and empowerment after choosing to have an abortion.
15.2. Abortion and Infertility
Abortion does not typically cause infertility. Safe, legal abortion procedures performed by trained medical professionals do not pose a significant risk to future fertility.
15.3. Abortion and Breast Cancer
There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that abortion increases the risk of breast cancer. Major medical organizations, such as the American Cancer Society, have concluded that there is no link between abortion and breast cancer risk.
16. The Future of Abortion Access
The future of abortion access in the United States and around the world remains uncertain, with ongoing legal and political challenges.
16.1. State-Level Battles
Many states are enacting laws that restrict or protect abortion access, leading to a patchwork of regulations across the country.
16.2. Federal Legislation
Efforts to codify the right to abortion into federal law could provide greater protection for abortion access nationwide.
16.3. Global Trends
Globally, the trend is toward greater liberalization of abortion laws, with many countries expanding access to safe and legal abortion services.
17. The Significance of Reproductive Justice
The concept of reproductive justice goes beyond the right to abortion and encompasses the broader social, economic, and political factors that affect reproductive health and well-being.
17.1. Defining Reproductive Justice
Reproductive justice is a framework that recognizes the right to have children, the right not to have children, and the right to parent children in safe and sustainable communities.
17.2. Addressing Systemic Inequalities
Reproductive justice seeks to address systemic inequalities that affect reproductive health, such as poverty, racism, and discrimination.
17.3. Promoting Empowerment
Reproductive justice empowers individuals and communities to make informed decisions about their reproductive health and advocate for policies that support reproductive freedom.
18. Ethical Considerations in Abortion Debates
Ethical considerations play a central role in debates about abortion, with different perspectives on the moral status of the fetus, the value of life, and the role of individual autonomy.
18.1. The Moral Status of the Fetus
One of the central ethical questions in abortion debates is the moral status of the fetus. Different perspectives range from viewing the fetus as a person with full moral rights from conception to viewing the fetus as having increasing moral status as it develops.
18.2. The Value of Life
Different perspectives on the value of life also shape ethical debates about abortion. Some believe that all human life is sacred and should be protected at all costs, while others prioritize the quality of life and individual autonomy.
18.3. Balancing Competing Values
Ethical debates about abortion often involve balancing competing values, such as the right to life, the right to bodily autonomy, and the right to reproductive freedom.
19. Public Health Implications of Abortion Policies
Abortion policies have significant public health implications, affecting maternal mortality rates, unintended pregnancies, and access to healthcare services.
19.1. Maternal Mortality Rates
Restricting abortion access can lead to an increase in maternal mortality rates, particularly in countries where unsafe abortions are common.
19.2. Unintended Pregnancies
Policies that restrict access to contraception and abortion can lead to higher rates of unintended pregnancies, which can have negative consequences for individuals, families, and communities.
19.3. Access to Healthcare Services
Abortion policies can affect access to healthcare services, particularly for low-income individuals and those living in rural areas.
20. The Importance of Evidence-Based Decision-Making
Making informed decisions about abortion policies requires careful consideration of scientific evidence, medical expertise, and the lived experiences of individuals and communities.
20.1. Relying on Scientific Evidence
Abortion policies should be based on scientific evidence, rather than ideology or personal beliefs. This includes evidence about the safety and effectiveness of abortion procedures, the impact of abortion policies on public health, and the lived experiences of individuals who have had abortions.
20.2. Consulting Medical Experts
Medical experts, such as obstetricians, gynecologists, and public health professionals, can provide valuable insights into the medical and public health implications of abortion policies.
20.3. Listening to Lived Experiences
Listening to the lived experiences of individuals who have had abortions is essential for understanding the complexities of reproductive decision-making and the impact of abortion policies on individuals and communities.
21. How Do Parental Notification Laws Impact Minors?
Parental notification laws require minors to obtain parental consent or notify their parents before having an abortion. These laws can have significant impacts on young people, particularly those who come from abusive or dysfunctional families.
21.1. Potential Benefits
Supporters of parental notification laws argue that they protect minors, promote family communication, and uphold parental rights.
21.2. Potential Harms
Opponents of parental notification laws argue that they can endanger minors, delay access to care, and violate their privacy. In some cases, minors may fear abuse, neglect, or abandonment if they disclose their pregnancy to their parents.
21.3. Judicial Bypass
Many parental notification laws include a judicial bypass option, which allows minors to seek permission from a judge to have an abortion without parental consent. However, navigating the judicial bypass process can be challenging and time-consuming.
22. What are the Long-Term Psychological Effects of Abortion?
The long-term psychological effects of abortion are a subject of ongoing debate and research. While some individuals may experience negative emotions after having an abortion, studies have shown that most do not suffer long-term psychological harm.
22.1. Factors Influencing Psychological Outcomes
Several factors can influence the psychological outcomes of abortion, including pre-existing mental health conditions, social support, and individual coping mechanisms.
22.2. Relief and Empowerment
Many individuals report feelings of relief and empowerment after having an abortion, particularly when they feel that they have made the right decision for themselves and their families.
22.3. Addressing Grief and Loss
For some individuals, abortion can be a source of grief and loss. Providing access to counseling and support services can help these individuals process their emotions and heal.
23. The Link Between Abortion and Contraception Access
Access to contraception is closely linked to abortion rates. When individuals have access to affordable and effective contraception, they are less likely to experience unintended pregnancies and seek abortions.
23.1. Reducing Unintended Pregnancies
Contraception can help reduce unintended pregnancies by preventing conception. When individuals have access to a range of contraceptive options, they can choose the method that best suits their needs and preferences.
23.2. Public Funding for Contraception
Public funding for contraception can help ensure that low-income individuals have access to affordable and effective contraception.
23.3. Comprehensive Sex Education
Comprehensive sex education can help individuals make informed decisions about contraception and reduce their risk of unintended pregnancy.
24. How Do Different Countries Approach Abortion Laws?
Different countries have adopted a wide range of approaches to abortion laws, ranging from highly restrictive to highly permissive.
24.1. Restrictive Laws
Some countries have highly restrictive abortion laws that prohibit abortion in all or most circumstances. These laws can lead to unsafe abortions and high rates of maternal mortality.
24.2. Permissive Laws
Other countries have permissive abortion laws that allow abortion on request or for a wide range of reasons. These laws are associated with lower rates of unsafe abortions and maternal mortality.
24.3. Moderate Laws
Many countries have moderate abortion laws that allow abortion in certain circumstances, such as to protect a woman’s health or in cases of rape or incest.
25. The Role of Advocacy Groups
Advocacy groups play a critical role in shaping public opinion and influencing abortion policies.
25.1. Supporting Abortion Rights
Groups that support abortion rights advocate for policies that protect and expand access to abortion services.
25.2. Opposing Abortion Rights
Groups that oppose abortion rights advocate for policies that restrict or prohibit abortion.
25.3. Promoting Dialogue
Some advocacy groups seek to promote dialogue and find common ground on the issue of abortion.
26. What are the Potential Economic Consequences of Banning Abortion?
Banning abortion could have significant economic consequences for individuals, families, and communities.
26.1. Increased Poverty
Banning abortion could lead to increased poverty rates, particularly for women and children.
26.2. Reduced Educational Attainment
Banning abortion could reduce educational attainment for women, particularly those who are forced to carry unintended pregnancies to term.
26.3. Strain on Social Services
Banning abortion could place additional strain on social services, such as welfare programs, childcare support, and adoption services.
27. The Impact of Abortion on Women’s Equality
Access to abortion is essential for women’s equality, allowing them to control their reproductive lives and participate fully in society.
27.1. Economic Empowerment
Access to abortion enables women to pursue their education and career goals, contributing to their economic empowerment.
27.2. Social Equality
Access to abortion allows women to make decisions about their reproductive health without government interference, promoting social equality.
27.3. Political Participation
Access to abortion enables women to participate fully in political life, advocating for policies that support their rights and well-being.
28. The Role of Men in Abortion Decisions
Men play an important role in abortion decisions, both as partners and as fathers.
28.1. Supporting Reproductive Choices
Men can support women’s reproductive choices by providing emotional and financial support, respecting their decisions, and advocating for policies that protect abortion access.
28.2. Shared Responsibility
Men share responsibility for preventing unintended pregnancies and supporting their partners in making informed reproductive choices.
28.3. Open Communication
Open communication between partners is essential for making responsible and informed decisions about reproductive health.
29. Addressing the Stigma Surrounding Abortion
Addressing the stigma surrounding abortion is essential for creating a supportive and compassionate environment for individuals facing reproductive choices.
29.1. Open Dialogue
Open dialogue about abortion can help reduce stigma and promote understanding.
29.2. Sharing Personal Stories
Sharing personal stories about abortion can help humanize the issue and challenge negative stereotypes.
29.3. Supporting Individuals
Supporting individuals who have had abortions can help them feel validated and empowered.
30. The Connection Between Abortion and Other Social Justice Issues
Abortion is connected to a range of other social justice issues, such as poverty, racism, and healthcare access.
30.1. Intersectionality
The concept of intersectionality recognizes that different forms of oppression are interconnected and can compound each other.
30.2. Addressing Systemic Inequalities
Addressing systemic inequalities is essential for promoting reproductive justice and ensuring that all individuals have access to the resources and opportunities they need to thrive.
30.3. Building Coalitions
Building coalitions with other social justice movements can help advance shared goals and create a more just and equitable society.
Abortion should remain legal to protect individual rights, health, and socioeconomic well-being. For reliable, expert answers to your questions about reproductive health and related topics, visit WHY.EDU.VN. Our team of professionals is dedicated to providing the information and support you need.
Key Takeaways
| Aspect | Summary |
|---|---|
| Bodily Autonomy | Legal abortion upholds the fundamental right of individuals to make autonomous decisions about their bodies. |
| Women’s Health | Legalizing abortion reduces unsafe practices and protects women’s health. |
| Socioeconomic Factors | Access to legal abortion supports economic stability and educational opportunities. |
| Rape and Incest Cases | Legal abortion provides a compassionate option for survivors of sexual violence. |
| Personal Beliefs & Values | Legal abortion respects individual beliefs and moral autonomy. |
FAQ: Common Questions About Abortion Legality
- Why is it important for abortion to be a legal option?
- Legal abortion protects reproductive freedom, ensures women’s health, and supports individual autonomy.
- How does legalizing abortion affect women’s health?
- Legalizing abortion significantly reduces the risk of unsafe practices and ensures procedures are performed by trained medical professionals.
- What are the socioeconomic factors linked to abortion access?
- Access to legal abortion enables individuals to pursue education, career aspirations, and aligns with financial capabilities.
- How does abortion relate to cases of rape and incest?
- Legal abortion provides a compassionate option for survivors to terminate pregnancies resulting from these violent acts.
- How do personal beliefs and values factor into the abortion debate?
- Legalizing abortion respects individual beliefs and moral autonomy, allowing people to make decisions consistent with their conscience.
- What impact do parental notification laws have on minors seeking abortions?
- Parental notification laws can endanger minors, delay access to care, and violate their privacy, especially in abusive situations.
- Are there long-term psychological effects of abortion?
- Studies show that most individuals do not suffer long-term psychological harm and may experience relief and empowerment.
- How does contraception access relate to abortion rates?
- Increased access to contraception reduces unintended pregnancies and the need for abortions.
- What are the potential economic consequences of banning abortion?
- Banning abortion could lead to increased poverty rates, reduced educational attainment, and strain social services.
- How does abortion impact women’s equality?
- Access to abortion is essential for women’s equality, economic empowerment, social equality, and political participation.
For more information, visit WHY.EDU.VN, where experts provide clear, comprehensive answers to your questions.
If you’re struggling to find reliable answers to complex questions, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at WHY.EDU.VN. Our team of experts is here to provide you with the knowledge and support you need. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. Reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (213) 555-0101, or visit our website at why.edu.vn to submit your questions today.