Are you constantly pushing tasks to the last minute, wondering, “But Why do I procrastinate?” At WHY.EDU.VN, we delve into the depths of this common struggle, offering insights and solutions to help you overcome procrastination and achieve your goals. Discover effective strategies, expert advice, and a supportive community to conquer your procrastination habits and unlock your full potential, improving your time management skills and overall productivity.
1. The Procrastination Puzzle: But Why Does It Happen?
Procrastination, the act of delaying or postponing tasks, affects people of all ages and backgrounds. But why do we do it, even when we know it can lead to negative consequences? Understanding the root causes of procrastination is the first step towards overcoming it.
- Fear of Failure: Many people procrastinate because they fear not meeting expectations or performing poorly. This fear can be paralyzing, leading to avoidance of the task altogether.
- Perfectionism: The pursuit of perfection can also lead to procrastination. Setting unrealistic standards can make a task seem overwhelming, causing individuals to delay starting or completing it.
- Lack of Motivation: When a task seems boring, unpleasant, or irrelevant, it’s easy to lose motivation and put it off.
- Difficulty Focusing: Distractions, attention deficits, and poor time management skills can make it challenging to concentrate on a task, leading to procrastination.
- Decision Paralysis: Overwhelmed by too many choices or a lack of clarity, some individuals may procrastinate as a way to avoid making a decision.
2. The Brain Science Behind Procrastination: But Why is it So Hard to Stop?
Neuroscience offers valuable insights into the biological mechanisms that drive procrastination. Understanding how the brain works can help us develop strategies to rewire our habits and overcome the urge to procrastinate.
- The Prefrontal Cortex: This brain region is responsible for planning, decision-making, and impulse control. Procrastination is often linked to reduced activity or connectivity in the prefrontal cortex.
- The Limbic System: This area of the brain is associated with emotions, pleasure, and immediate gratification. When faced with a challenging task, the limbic system may override the prefrontal cortex, leading us to seek out more pleasurable activities instead.
- Dopamine: This neurotransmitter plays a key role in motivation and reward. Procrastination can be a way to seek a quick dopamine fix, even if it means sacrificing long-term goals.
- Amygdala: This brain structure processes fear and anxiety. When faced with a task that triggers negative emotions, the amygdala can activate avoidance behaviors, leading to procrastination.
3. Types of Procrastinators: But Why Do I Procrastinate This Way?
Procrastination manifests in different ways, and understanding your specific procrastination style can help you tailor your approach to overcoming it. Here are some common types of procrastinators:
| Type of Procrastinator | Description | Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| The Perfectionist | Sets unrealistically high standards and fears not meeting them. | Challenge perfectionistic thinking, break tasks into smaller steps, focus on progress rather than perfection. |
| The Dreamer | Has big ideas but struggles to translate them into action. | Set realistic goals, create a detailed plan, focus on taking small steps forward. |
| The Worrier | Feels overwhelmed by anxiety and uncertainty, leading to avoidance. | Practice relaxation techniques, challenge negative thoughts, seek support from others. |
| The Crisis-Maker | Thrives on the adrenaline rush of last-minute deadlines. | Create artificial deadlines, reward yourself for completing tasks on time, learn to manage your time effectively. |
| The Defier | Resists authority or external expectations, leading to procrastination as a form of rebellion. | Find intrinsic motivation, set your own goals, focus on the benefits of completing the task. |
4. The Impact of Procrastination: But Why is it a Problem?
Procrastination can have far-reaching consequences, affecting not only our productivity but also our mental and physical well-being.
- Increased Stress and Anxiety: Delaying tasks can lead to a build-up of stress and anxiety as deadlines approach.
- Reduced Performance: Last-minute work often results in lower quality and missed opportunities.
- Damaged Relationships: Procrastination can strain relationships with colleagues, friends, and family members.
- Health Problems: Chronic stress associated with procrastination can contribute to various health issues, such as headaches, digestive problems, and sleep disturbances.
- Lost Opportunities: Procrastination can prevent us from pursuing our goals and dreams, leading to feelings of regret and unfulfilled potential.
5. How To Stop Procrastinating: But Why Can’t I Just Stop?
Breaking free from procrastination requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses the underlying causes and develops effective coping strategies. Here are some evidence-based techniques to help you overcome procrastination:
- Identify Your Triggers: Recognize the situations, thoughts, and feelings that lead to procrastination.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break large tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
- Prioritize Tasks: Focus on the most important and urgent tasks first.
- Create a Schedule: Allocate specific times for working on tasks and stick to your schedule as much as possible.
- Minimize Distractions: Turn off notifications, close unnecessary tabs, and create a dedicated workspace.
- Use Time Management Techniques: Experiment with methods like the Pomodoro Technique, time blocking, or the Eisenhower Matrix.
- Reward Yourself: Celebrate your accomplishments, no matter how small.
- Practice Self-Compassion: Be kind to yourself and avoid self-criticism when you procrastinate.
- Seek Support: Talk to a therapist, coach, or friend who can help you identify and address your procrastination habits.
6. The Eisenhower Matrix: But Why Is This So Effective for Time Management?
The Eisenhower Matrix, also known as the Urgent-Important Matrix, is a powerful tool for prioritizing tasks and overcoming procrastination. It involves categorizing tasks based on their urgency and importance, helping you focus on what truly matters.
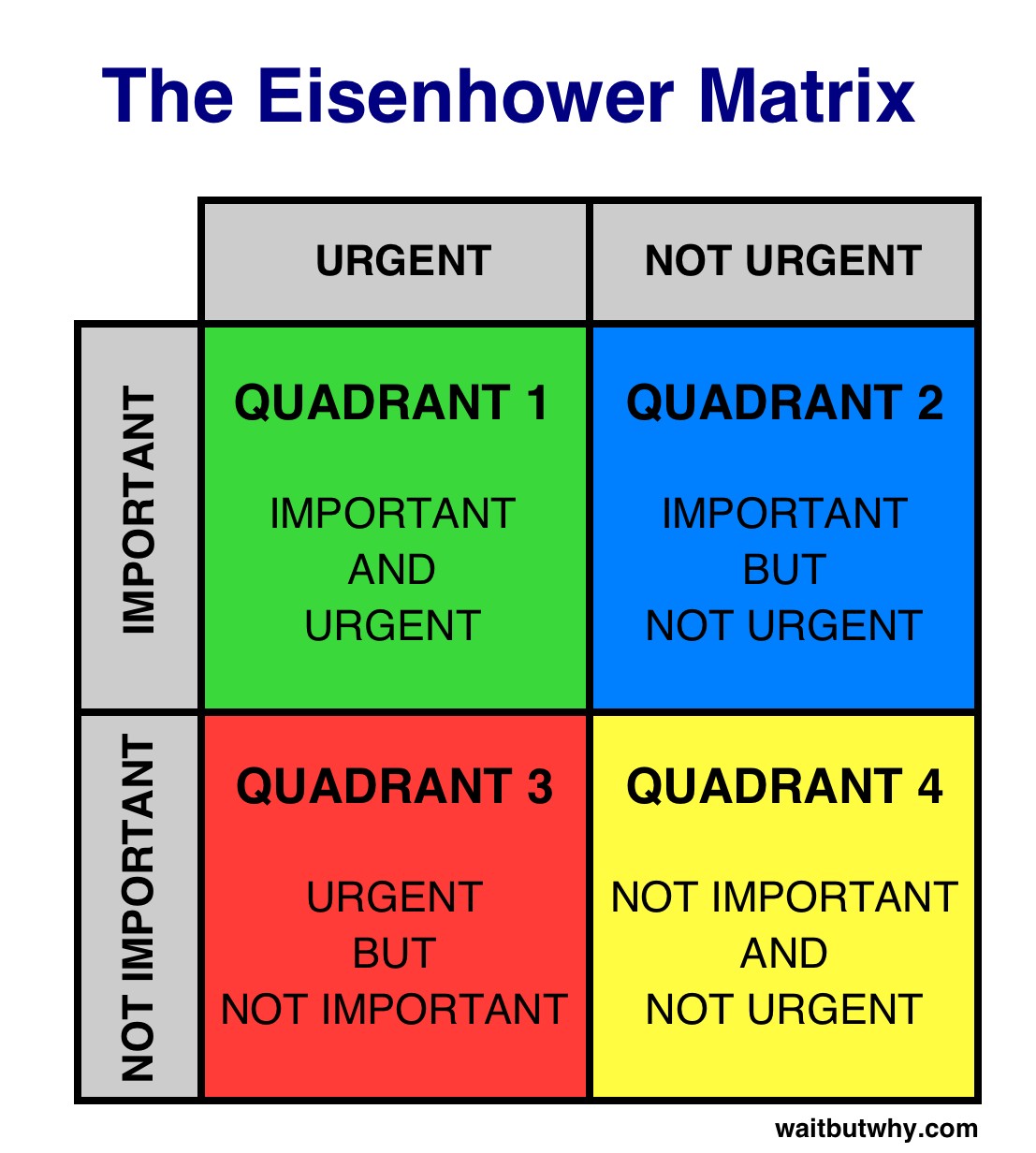 Eisenhower Matrix
Eisenhower Matrix
- Quadrant 1: Urgent and Important (Do First): These are tasks that require immediate attention, such as crises, deadlines, and emergencies.
- Quadrant 2: Important but Not Urgent (Schedule): These are tasks that contribute to your long-term goals, such as planning, relationship building, and personal development.
- Quadrant 3: Urgent but Not Important (Delegate): These are tasks that demand immediate attention but don’t contribute to your goals, such as interruptions, some meetings, and certain emails.
- Quadrant 4: Not Urgent and Not Important (Eliminate): These are tasks that are time-wasters and distractions, such as mindless browsing, excessive social media use, and trivial activities.
By using the Eisenhower Matrix, you can prioritize your tasks, delegate or eliminate those that are not essential, and focus your time and energy on activities that truly matter.
7. Time Management Techniques: But Why Don’t They Always Work?
While time management techniques can be helpful, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s important to find the techniques that work best for you and adapt them to your individual needs and preferences.
- The Pomodoro Technique: This technique involves working in focused 25-minute intervals, followed by a short break.
- Time Blocking: This method involves scheduling specific blocks of time for different tasks.
- Getting Things Done (GTD): This system focuses on capturing, organizing, and prioritizing tasks to reduce stress and increase productivity.
- The Two-Minute Rule: If a task takes less than two minutes, do it immediately.
If a time management technique doesn’t work for you, don’t give up. Experiment with different methods until you find one that aligns with your workflow and helps you stay on track.
8. The Role of Self-Compassion: But Why Should I Be Kind To Myself When I Procrastinate?
Self-compassion, the practice of treating yourself with kindness, understanding, and acceptance, can be a powerful antidote to procrastination. When you procrastinate, it’s easy to fall into a cycle of self-criticism and shame, which can make it even harder to get started.
By practicing self-compassion, you can break this cycle and create a more supportive inner environment. Instead of berating yourself for procrastinating, acknowledge your struggles, remind yourself that everyone procrastinates sometimes, and offer yourself encouragement and support.
9. Overcoming Perfectionism: But Why Can’t I Just Do It Perfectly?
Perfectionism, the relentless pursuit of flawlessness, can be a major driver of procrastination. Setting unrealistic standards can make tasks seem overwhelming, leading to avoidance and delay.
To overcome perfectionism, it’s important to:
- Challenge perfectionistic thoughts: Recognize that perfection is unattainable and that mistakes are a natural part of the learning process.
- Set realistic goals: Break tasks into smaller, manageable steps and focus on progress rather than perfection.
- Embrace imperfection: Accept that good enough is often better than perfect and that it’s okay to make mistakes.
- Focus on the process: Enjoy the process of learning and growing, rather than solely focusing on the outcome.
10. Creating a Supportive Environment: But Why Does My Environment Matter?
Your environment can have a significant impact on your ability to focus and avoid procrastination. Creating a supportive environment can help you stay on track and achieve your goals.
- Minimize distractions: Choose a quiet workspace where you won’t be interrupted.
- Organize your space: Keep your workspace tidy and clutter-free.
- Optimize lighting and temperature: Ensure your workspace is well-lit and at a comfortable temperature.
- Use technology wisely: Turn off notifications, block distracting websites, and use productivity apps to stay focused.
- Surround yourself with supportive people: Seek out friends, family members, or colleagues who can encourage and motivate you.
11. The Power of Accountability: But Why Do I Need Someone to Hold Me Accountable?
Accountability, the act of being responsible for your actions and commitments, can be a powerful tool for overcoming procrastination. When you know that someone else is counting on you, you’re more likely to follow through on your plans.
- Find an accountability partner: Ask a friend, family member, or colleague to check in with you regularly and provide support and encouragement.
- Join a group: Participate in a procrastination support group or online forum.
- Hire a coach: Work with a professional coach who can help you set goals, develop strategies, and stay on track.
- Publicly commit to your goals: Announce your goals to others to increase your motivation and commitment.
12. Reframing Your Mindset: But Why Is My Attitude So Important?
Your mindset, the way you think about yourself and your abilities, can have a profound impact on your ability to overcome procrastination. A positive and growth-oriented mindset can help you approach challenges with confidence and resilience.
- Challenge negative thoughts: Recognize and challenge negative thoughts that contribute to procrastination, such as “I can’t do this” or “I’m going to fail.”
- Focus on your strengths: Identify your strengths and focus on using them to overcome challenges.
- Embrace a growth mindset: Believe that your abilities can be developed through effort and learning.
- Practice gratitude: Focus on the positive aspects of your life and express gratitude for what you have.
- Visualize success: Imagine yourself successfully completing tasks and achieving your goals.
13. Addressing Underlying Issues: But Why Is Procrastination a Symptom of Something Deeper?
Sometimes, procrastination can be a symptom of underlying issues, such as anxiety, depression, ADHD, or learning disabilities. If you suspect that your procrastination is related to a more serious problem, it’s important to seek professional help.
- Consult a therapist: A therapist can help you identify and address the underlying causes of your procrastination.
- Talk to a doctor: A doctor can assess whether your procrastination is related to a medical condition or medication side effects.
- Seek educational support: If you have a learning disability, seek support from a qualified professional.
14. The Importance of Self-Care: But Why Do I Need to Take Care of Myself to Stop Procrastinating?
Self-care, the practice of taking care of your physical, mental, and emotional well-being, is essential for overcoming procrastination. When you’re well-rested, nourished, and emotionally balanced, you’re better able to focus, manage stress, and resist the urge to procrastinate.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Eat a healthy diet: Nourish your body with nutritious foods that provide sustained energy.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity can reduce stress, improve mood, and boost cognitive function.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help calm your mind and reduce anxiety.
- Engage in enjoyable activities: Make time for hobbies, social activities, and other things that bring you joy.
15. The Long-Term Perspective: But Why Is It Worth the Effort to Overcome Procrastination?
Overcoming procrastination is not a quick fix but a long-term process that requires commitment, patience, and self-compassion. However, the rewards of overcoming procrastination are well worth the effort.
- Increased Productivity: You’ll be able to accomplish more in less time, freeing up time for other pursuits.
- Reduced Stress and Anxiety: You’ll experience less stress and anxiety as you gain control over your time and tasks.
- Improved Relationships: You’ll be able to fulfill your commitments and strengthen your relationships.
- Enhanced Well-being: You’ll experience greater satisfaction, confidence, and overall well-being.
- Achieved Goals: You’ll be able to pursue your dreams and achieve your full potential.
Procrastination is a common challenge, but it is not insurmountable. By understanding the causes of procrastination, developing effective strategies, and cultivating a supportive mindset, you can overcome this habit and unlock your full potential.
Don’t let procrastination hold you back any longer. Visit WHY.EDU.VN today to discover more resources, expert advice, and a supportive community to help you conquer your procrastination habits and achieve your goals. At WHY.EDU.VN, we offer in-depth knowledge and answers, helping you to ask, and answer the pivotal question “But Why?” and more. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101.
Let why.edu.vn be your guide on the path to a more productive and fulfilling life. Find out more today.
FAQ: Common Questions About Procrastination
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is procrastination? | Procrastination is the act of delaying or postponing tasks, often leading to negative consequences. |
| Why do people procrastinate? | Procrastination can be caused by fear of failure, perfectionism, lack of motivation, difficulty focusing, and other factors. |
| What are the consequences of procrastination? | Procrastination can lead to increased stress, reduced performance, damaged relationships, health problems, and lost opportunities. |
| How can I stop procrastinating? | You can stop procrastinating by identifying your triggers, setting realistic goals, prioritizing tasks, creating a schedule, minimizing distractions, using time management techniques, rewarding yourself, practicing self-compassion, and seeking support. |
| What is the Eisenhower Matrix? | The Eisenhower Matrix is a tool for prioritizing tasks based on their urgency and importance. |
| How can self-compassion help with procrastination? | Self-compassion can help break the cycle of self-criticism and shame that often accompanies procrastination. |
| How does perfectionism contribute to procrastination? | Perfectionism can lead to procrastination by making tasks seem overwhelming and unattainable. |
| How does my environment affect procrastination? | Your environment can have a significant impact on your ability to focus and avoid procrastination. |
| Why is accountability important for overcoming it? | Accountability can help you stay on track and follow through on your plans by creating a sense of responsibility to others. |
| Can procrastination be a sign of a deeper problem? | Yes, procrastination can sometimes be a symptom of underlying issues such as anxiety, depression, ADHD, or learning disabilities. If you suspect this is the case, it’s important to seek professional help. |

