Cancer’s increasing prevalence is a concern for many, and understanding the reasons behind it is crucial; WHY.EDU.VN can shed light on this complex issue. The rise in cancer cases is primarily due to increased life expectancy and lifestyle factors, alongside genetics and environmental influences. Let’s explore why cancer is becoming more common, examining risk factors, lifestyle choices, and genetic predispositions, offering insight and awareness for a healthier future, supported by expert resources available at WHY.EDU.VN.
1. What is the Current Cancer Rate Globally?
The global cancer rate is increasing, with approximately 1 in 2 people likely to develop some form of cancer in their lifetime. This increase is attributed to factors like aging populations, lifestyle changes, and environmental factors.
Cancer is a disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. It can occur anywhere in the body and is caused by genetic mutations or abnormalities within cells. These mutations can be inherited, caused by environmental factors, or occur randomly. Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, but advances in prevention, detection, and treatment have improved survival rates for many types of cancer. Understanding the disease, its risk factors, and available treatments is crucial for reducing its impact on individuals and communities. For more detailed explanations and comprehensive resources, visit WHY.EDU.VN, where experts provide clear, reliable information.
1.1 How Has the Cancer Rate Changed Over Time?
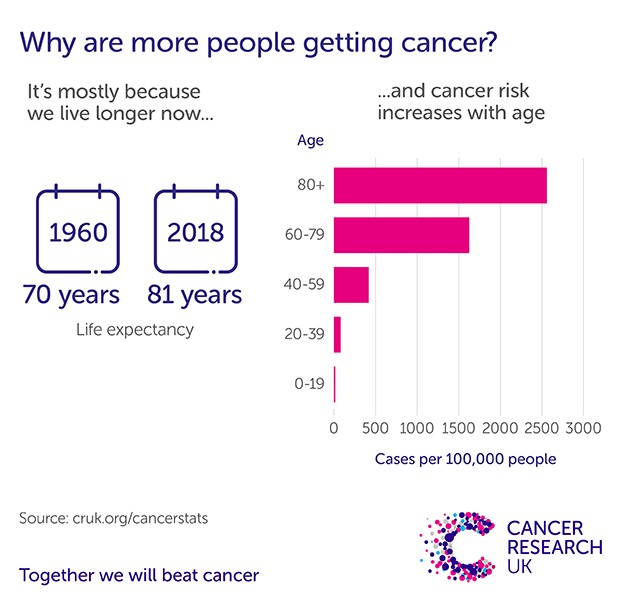
Cancer rates have risen significantly over the past few decades. According to a study published in the British Journal of Cancer, the lifetime risk of developing cancer for individuals born in 1930 was approximately 1 in 3. However, for those born in 1960, this risk increased to 1 in 2. This change reflects increasing life expectancy and shifts in lifestyle and environmental exposures. This trend underscores the importance of understanding the factors driving cancer prevalence and implementing effective prevention and early detection strategies.
1.2 What are the Most Common Types of Cancer?
The most common types of cancer vary by gender and region. In general, the most frequently diagnosed cancers include:
- Breast Cancer: Most common among women globally.
- Lung Cancer: Leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide, affecting both men and women.
- Prostate Cancer: Common among men, particularly in Western countries.
- Colorectal Cancer: Affects both men and women and is often linked to lifestyle factors.
- Skin Cancer: Incidence is rising due to increased UV exposure.
Understanding these common cancer types helps in focusing prevention and early detection efforts. At WHY.EDU.VN, you can find detailed information and expert advice on each type of cancer.
2. Why Are Cancer Rates Increasing?
The increase in cancer rates can be attributed to several key factors, including aging populations, lifestyle changes, and improvements in diagnostic methods. Let’s explore each of these in detail.
2.1 How Does Aging Affect Cancer Risk?
Aging is one of the most significant risk factors for cancer. As people live longer, they accumulate more genetic mutations over time, increasing the likelihood of cells becoming cancerous. According to Cancer Research UK, more than three-quarters of all people diagnosed with cancer are 60 years or older. The longer we live, the more opportunities there are for errors to build up in our DNA, leading to the development of cancer.
2.2 What Role Do Lifestyle Factors Play?
Lifestyle factors significantly influence cancer risk. These include diet, physical activity, tobacco and alcohol consumption, and exposure to environmental pollutants.
- Diet: A diet high in processed foods, red meat, and low in fruits and vegetables can increase the risk of certain cancers, such as colorectal cancer.
- Physical Activity: Lack of physical activity is associated with a higher risk of several cancers, including breast, colon, and endometrial cancers.
- Tobacco and Alcohol: Smoking is the leading preventable cause of cancer, responsible for a significant percentage of cancer deaths. Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of liver, breast, and other cancers.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, radiation, and certain chemicals can also contribute to cancer development.
2.3 How Do Improved Diagnostic Methods Influence Cancer Rates?
Advances in diagnostic technologies, such as mammography, colonoscopy, and PSA testing, have led to earlier and more frequent detection of cancers. While this doesn’t necessarily mean more people are developing cancer, it does mean that more cases are being identified and diagnosed, contributing to higher reported incidence rates. Early detection often leads to better treatment outcomes and improved survival rates.
2.4 The Role of Infections
Certain infections play a significant role in increasing the risk of specific cancers. Viruses like Human Papillomavirus (HPV), Hepatitis B and C, and bacteria such as Helicobacter pylori are known to elevate cancer risk.
- HPV (Human Papillomavirus): HPV is a common virus that can cause cervical, anal, and other types of cancer. Vaccination against HPV has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
- Hepatitis B and C: Chronic infections with Hepatitis B and C viruses can lead to liver cancer. Vaccination and antiviral treatments are crucial in preventing these infections and reducing the risk of liver cancer.
- Helicobacter pylori: This bacterium can cause stomach ulcers and increase the risk of stomach cancer. Antibiotic treatment to eradicate H. pylori infection can lower the risk of developing stomach cancer.
Preventing and managing these infections through vaccination, screening, and treatment is essential in reducing the incidence of associated cancers.
3. Specific Cancers and Their Risk Factors
Different types of cancer have specific risk factors that contribute to their prevalence. Understanding these factors can help in implementing targeted prevention strategies.
3.1 Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women worldwide. Key risk factors include:
- Age: The risk of breast cancer increases with age.
- Family History: Having a family history of breast cancer increases the risk.
- Hormonal Factors: Early menstruation, late menopause, and hormone replacement therapy can increase the risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity are also risk factors.
- Breastfeeding: Studies show that breastfeeding can lower the risk of breast cancer.
Breast screening programs have led to earlier detection and improved survival rates. However, lifestyle modifications and awareness are crucial in reducing the risk.
3.2 Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths globally. The primary risk factor is smoking, but other factors also contribute.
- Smoking: Responsible for the majority of lung cancer cases.
- Exposure to Radon: Radon is a radioactive gas that can increase the risk of lung cancer.
- Occupational Exposures: Exposure to asbestos and other chemicals in the workplace can increase the risk.
- Air Pollution: Long-term exposure to air pollution can also contribute.
Efforts to reduce smoking rates and improve air quality are essential in preventing lung cancer.
3.3 Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is common among men, particularly in developed countries. Risk factors include:
- Age: The risk increases with age.
- Family History: Having a family history of prostate cancer increases the risk.
- Race: African American men have a higher risk.
- Diet: A diet high in fat may increase the risk.
PSA testing has led to increased detection of prostate cancer, but there is ongoing debate about the benefits and risks of screening.
3.4 Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer affects both men and women and is often linked to lifestyle factors. Key risk factors include:
- Age: The risk increases with age.
- Family History: Having a family history of colorectal cancer increases the risk.
- Diet: A diet high in red and processed meat and low in fiber increases the risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, physical inactivity, and smoking are also risk factors.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis increase the risk.
Regular screening, including colonoscopy, is crucial for early detection and prevention.
3.5 Skin Cancer
Skin cancer incidence is rising, primarily due to increased UV exposure. Key risk factors include:
- UV Exposure: Exposure to sunlight and tanning beds is the main risk factor.
- Fair Skin: People with fair skin, freckles, and light hair are at higher risk.
- Family History: Having a family history of skin cancer increases the risk.
- Multiple Moles: Having many moles can increase the risk.
Protecting the skin from UV radiation through sunscreen use and avoiding tanning beds is essential in preventing skin cancer.
4. How Can We Reduce Cancer Risk?
While some risk factors like age and genetics are beyond our control, there are many lifestyle changes and preventive measures we can take to reduce our risk of developing cancer.
4.1 Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly lower cancer risk. Key modifications include:
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limiting processed foods, red meat, and sugary drinks.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of several cancers.
- Avoid Tobacco: Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke is crucial.
- Limit Alcohol: Reducing alcohol consumption can lower the risk of liver, breast, and other cancers.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of several cancers.
4.2 Screening and Early Detection
Regular screening can detect cancer early, when it is most treatable. Recommended screenings include:
- Mammograms: For breast cancer detection in women.
- Colonoscopies: For colorectal cancer detection in men and women.
- PSA Tests: For prostate cancer detection in men (discuss with your doctor).
- Pap Tests: For cervical cancer detection in women.
- Skin Exams: Regular self-exams and professional exams for skin cancer detection.
4.3 Vaccination
Vaccinations can protect against certain viruses that increase cancer risk. Key vaccines include:
- HPV Vaccine: Prevents cervical, anal, and other HPV-related cancers.
- Hepatitis B Vaccine: Prevents liver cancer caused by Hepatitis B infection.
4.4 Environmental Awareness
Reducing exposure to environmental risk factors can also lower cancer risk. This includes:
- Radon Mitigation: Testing homes for radon and mitigating if levels are high.
- Air Quality: Supporting policies to improve air quality and reduce pollution.
- Sun Protection: Protecting the skin from UV radiation through sunscreen and protective clothing.
By implementing these preventive measures, individuals and communities can significantly reduce the burden of cancer.
5. The Impact of Research and Innovation
Ongoing research and innovation are crucial for improving cancer prevention, detection, and treatment. Advances in genetics, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies offer new hope for patients.
5.1 Genetic Research
Understanding the genetic basis of cancer is leading to new ways to identify individuals at high risk and develop personalized treatments. Genetic testing can help identify inherited mutations that increase cancer risk, allowing for earlier screening and preventive measures.
5.2 Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer. This approach has shown remarkable success in treating certain types of cancer, such as melanoma and lung cancer.
5.3 Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies are drugs that specifically target cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells. These therapies are often more effective and have fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
5.4 Early Detection Technologies
New technologies, such as liquid biopsies, are being developed to detect cancer early through blood tests. These tests can identify cancer DNA or cancer cells in the bloodstream, allowing for earlier diagnosis and treatment.
Continued investment in cancer research and innovation is essential for improving outcomes and reducing the impact of this disease.
6. Addressing Health Disparities in Cancer Rates
Health disparities exist in cancer rates, with certain populations experiencing higher incidence and mortality rates. Addressing these disparities is crucial for achieving health equity.
6.1 Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors, such as poverty and lack of access to healthcare, can contribute to higher cancer rates in certain communities. Addressing these factors requires comprehensive strategies to improve access to education, employment, and healthcare.
6.2 Cultural and Linguistic Barriers
Cultural and linguistic barriers can also hinder access to cancer prevention and treatment services. Providing culturally sensitive education and outreach programs, as well as translation services, can help overcome these barriers.
6.3 Geographic Disparities
Geographic disparities exist in cancer rates, with rural areas often having higher incidence and mortality rates. Improving access to healthcare in rural areas, through telemedicine and mobile screening units, can help reduce these disparities.
6.4 Racial and Ethnic Disparities
Racial and ethnic minorities often experience higher cancer rates and poorer outcomes. Addressing these disparities requires culturally competent care, targeted prevention programs, and research to understand the underlying causes of these differences.
7. The Role of Public Health Initiatives
Public health initiatives play a crucial role in preventing and controlling cancer. These initiatives include:
7.1 Cancer Prevention Campaigns
Public health campaigns can raise awareness about cancer risk factors and promote healthy behaviors. These campaigns often focus on topics such as smoking cessation, healthy eating, and sun protection.
7.2 Screening Programs
Government-sponsored screening programs can help detect cancer early, when it is most treatable. These programs often target specific populations at high risk for certain cancers.
7.3 Policy and Legislation
Policy and legislation can support cancer prevention and control efforts. This includes policies to reduce smoking rates, improve air quality, and promote access to healthcare.
7.4 Community-Based Interventions
Community-based interventions can address cancer risk factors at the local level. These interventions often involve partnerships between healthcare providers, community organizations, and local governments.
8. Support and Resources for Cancer Patients and Families
Cancer can have a significant impact on patients and their families. Access to support and resources is essential for coping with the emotional, physical, and financial challenges of the disease.
8.1 Emotional Support
Emotional support groups and counseling services can help patients and families cope with the emotional stress of cancer. These resources provide a safe space to share feelings and experiences with others who understand.
8.2 Financial Assistance
Financial assistance programs can help patients and families manage the costs of cancer treatment. These programs may provide assistance with medical bills, transportation, and other expenses.
8.3 Practical Support
Practical support services, such as transportation, childcare, and meal delivery, can help patients and families manage the daily challenges of cancer treatment.
8.4 Information and Education
Reliable information and education about cancer can help patients and families make informed decisions about their care. This includes information about treatment options, side effects, and supportive care services.
9. The Future of Cancer Prevention and Treatment
The future of cancer prevention and treatment is promising, with ongoing research and innovation leading to new approaches for early detection, personalized therapies, and improved outcomes.
9.1 Precision Medicine
Precision medicine tailors treatment to the individual, based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment. This approach has the potential to improve outcomes and reduce side effects.
9.2 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to analyze large datasets and identify patterns that can help improve cancer detection, diagnosis, and treatment. AI can also be used to develop new drugs and therapies.
9.3 Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is being used to develop new ways to deliver drugs directly to cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells. This approach has the potential to improve the effectiveness of cancer treatment and reduce side effects.
9.4 Cancer Vaccines
Cancer vaccines are being developed to stimulate the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. These vaccines have the potential to prevent cancer from developing or recurring.
10. Call to Action
Understanding why cancer is so common is the first step in taking action to reduce your risk and support those affected by this disease. At WHY.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the information and resources you need to make informed decisions about your health. We are dedicated to answering all your questions and providing expert insights to help you navigate the complexities of cancer.
10.1 Take Control of Your Health
Adopt a healthy lifestyle, get regular screenings, and stay informed about the latest advances in cancer prevention and treatment.
10.2 Support Cancer Research
Donate to cancer research organizations and advocate for policies that support cancer prevention and control efforts.
10.3 Spread Awareness
Share information about cancer risk factors and prevention strategies with your friends, family, and community.
10.4 Seek Information at WHY.EDU.VN
Visit WHY.EDU.VN for detailed answers and expert guidance on cancer-related questions.
By working together, we can reduce the burden of cancer and improve the lives of those affected by this disease.
If you have more questions or need further assistance, visit us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101, or explore our website at WHY.EDU.VN. Our team of experts is ready to provide you with the knowledge and support you need.
FAQ About Cancer Prevalence
Here are some frequently asked questions about cancer prevalence and related topics:
1. What is the lifetime risk of developing cancer?
The lifetime risk of developing cancer is approximately 1 in 2 for individuals born after 1960.
2. Why are cancer rates increasing?
Cancer rates are increasing due to factors such as aging populations, lifestyle changes, and improved diagnostic methods.
3. What are the most common types of cancer?
The most common types of cancer include breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, colorectal cancer, and skin cancer.
4. How can I reduce my risk of developing cancer?
You can reduce your risk by adopting a healthy lifestyle, getting regular screenings, and staying informed about cancer prevention strategies.
5. What is the role of genetics in cancer risk?
Genetics play a significant role in cancer risk, with certain inherited mutations increasing the likelihood of developing cancer.
6. How does smoking affect cancer risk?
Smoking is the leading preventable cause of cancer, responsible for a significant percentage of cancer deaths.
7. What is the importance of early detection in cancer treatment?
Early detection can lead to better treatment outcomes and improved survival rates.
8. How does obesity affect cancer risk?
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of several cancers, including breast, colon, and endometrial cancers.
9. What is immunotherapy, and how does it help in cancer treatment?
Immunotherapy harnesses the power of the immune system to fight cancer and has shown remarkable success in treating certain types of cancer.
10. Where can I find reliable information and support for cancer-related questions?
You can find reliable information and support at why.edu.vn, where experts provide clear, accurate, and comprehensive resources.