Dreams are a fascinating and enigmatic aspect of our sleep. At WHY.EDU.VN, we delve into the science and psychology behind them to understand why they occur. Let’s explore the latest research and theories to shed light on the question of Why Do Dreams Happen, unraveling the complexities of our nocturnal mental landscape and offering clarity on dream analysis and dream interpretation. Discover the secrets of your dreaming mind with insights into sleep cycles, REM sleep, and the purpose of dreaming.
1. What Exactly Are Dreams?
Dreams are essentially a series of images, thoughts, emotions, and sensations that occur involuntarily in the mind during certain stages of sleep. While visual elements tend to be the most dominant, dreams can engage all of our senses, offering a rich and immersive experience. It’s important to remember that dream recall varies significantly among individuals.
1.1. Sensory Experiences
Dreams aren’t limited to just visual experiences. They can encompass sounds, tastes, smells, and tactile sensations, providing a holistic and multi-sensory experience. Some individuals report vivid color dreams, while others experience dreams in black and white. Blind individuals often have dreams that emphasize sound, taste, and smell.
1.2. Common Characteristics of Dreams
While dream content varies greatly from person to person, some typical characteristics of dreaming include:
- First-Person Perspective: Dreams are typically experienced from a first-person viewpoint, immersing the dreamer directly in the narrative.
- Involuntary Nature: Dreams occur spontaneously, without conscious control or effort.
- Illogical or Incoherent Content: Dream content can often be illogical, bizarre, or nonsensical, defying the constraints of waking-world reality.
- Interactions with Others: Dreams often feature interactions with other people, real or imagined, who engage with the dreamer and with each other.
- Strong Emotions: Dreams can evoke a wide range of intense emotions, from joy and excitement to fear and anxiety.
- Incorporation of Waking-Life Elements: Dreams frequently incorporate elements from the dreamer’s waking life, such as people, places, events, and concerns.
While these features are commonly observed in dreams, they aren’t universally present in every dream experience.
2. What Is The Science Behind Why Do We Dream?
The precise reasons why we dream remain a subject of debate among sleep experts. However, several prominent theories attempt to explain the purpose and function of dreaming.
2.1. Theories About the Purpose of Dreaming
Several theories attempt to explain the purpose of dreaming:
- Memory Consolidation: Dreaming has been linked to memory consolidation, suggesting that it may play a crucial role in strengthening memories and facilitating information recall.
- Emotional Processing: Dreams may provide a safe space for processing emotions, allowing the brain to rehearse feelings in different imagined contexts as a way of managing and regulating emotions.
- Mental Housekeeping: Dreaming could be a form of mental “housekeeping,” where the brain clears away unnecessary, erroneous, or partial information to optimize cognitive function.
- Instant Replay: Dream content may serve as a distorted instant replay of recent events, allowing the brain to review and analyze experiences.
- Incidental Brain Activity: This theory suggests that dreaming is simply a byproduct of brain activity during sleep, with no essential purpose or meaning.
2.2. Ongoing Research
Neuroscience and psychology experts are actively engaged in research to uncover the neural mechanisms underlying sleep and dreaming. Despite ongoing efforts, conclusively proving any single theory for why we dream may remain elusive.
3. When Do Dreams Typically Occur?
On average, people dream for approximately two hours each night. Dreaming can occur during any stage of sleep, but it is most frequent and intense during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage.
3.1. REM Sleep and Dreaming
During REM sleep, brain activity surges considerably compared to non-REM sleep stages. This heightened brain activity explains why the distinct types of dreaming occur during these stages.
Dreams during REM sleep are typically vivid, fantastical, and bizarre, often incorporating elements of waking life. In contrast, non-REM dreams tend to feature more coherent content involving thoughts or memories grounded in a specific time and place.
3.2. Distribution of REM Sleep
REM sleep is not evenly distributed throughout the night. It predominates during the second half of a normal sleep period, meaning that dreaming is concentrated in the hours leading up to waking up.
4. Is There Meaning Behind Our Dreams?
The interpretation of dreams and whether they hold any inherent meaning is a contentious topic. While some psychologists argue that dreams offer insights into a person’s psyche or everyday life, others consider their content too inconsistent and perplexing to reliably convey meaning.
4.1. Connections to Waking Life
Most experts agree that dreams can involve content that relates back to waking experiences, although the content may be altered or misrepresented. For instance, people often recognize familiar individuals in their dreams, even if their appearance is distorted.
4.2. The Continuity and Discontinuity Hypotheses
The “continuity hypothesis” suggests that dreams and waking life are interconnected, with overlapping themes and content. Conversely, the “discontinuity hypothesis” posits that thinking during dreams and wakefulness are structurally distinct.
4.3. Subjective Interpretation
While dream analysis can be a valuable tool for personal or psychological self-reflection, there’s no definitive method for interpreting and understanding the meaning of dreams in waking life based on current evidence.
5. What Are the Different Types of Dreams?
Dreams manifest in various forms, each with its unique characteristics.
5.1. Common Types of Dreams
- Lucid Dreams: Lucid dreams occur when a person is aware that they are dreaming while still in the dream state.
- Vivid Dreams: Vivid dreams are characterized by their intense realism and clarity.
- Bad Dreams: Bad dreams are dreams that contain bothersome or distressing content.
- Recurring Dreams: Recurring dreams involve the same imagery repeating in multiple dreams over time.
5.2. Common Dream Themes
Even within normal dreams, certain themes are particularly common and recognizable, such as flying, falling, being chased, or being unable to find a bathroom.
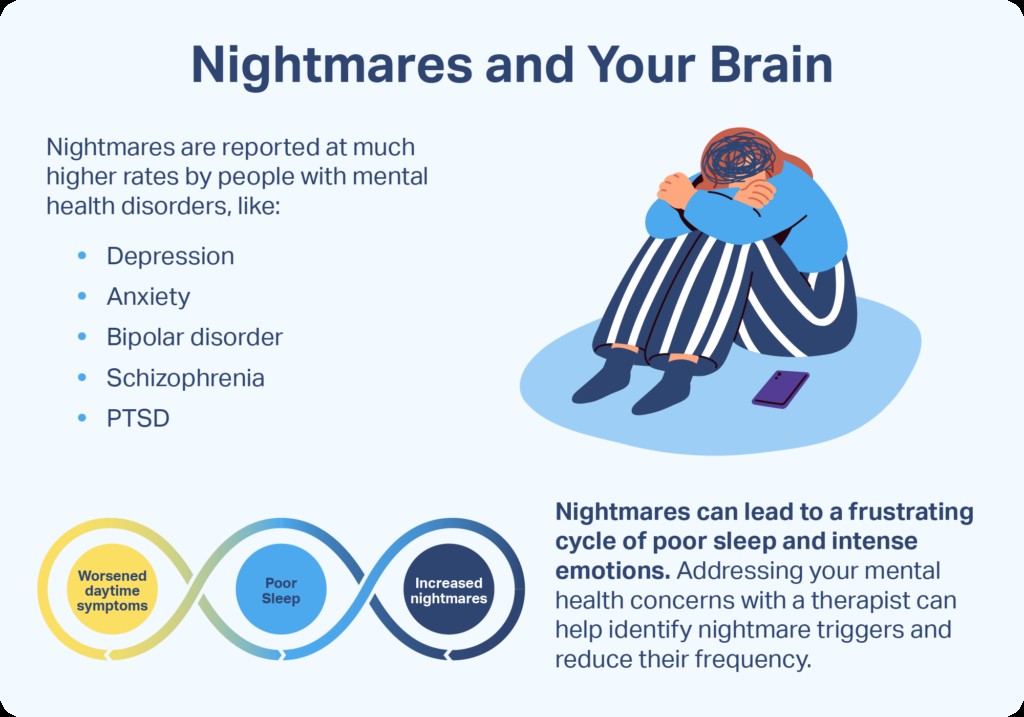
6. What About Nightmares?
In sleep medicine, a nightmare is defined as a bad dream that causes a person to wake up from sleep.
6.1. Nightmares vs. Bad Dreams
This definition differs from common usage, where any threatening, scary, or bothersome dream may be referred to as a nightmare. While bad dreams are normal and usually harmless, frequent nightmares can disrupt sleep and lead to impaired thinking and mood during the daytime.
7. Do Dreams Impact Our Sleep Quality?
In most instances, dreams don’t negatively affect sleep. Dreaming is a natural part of healthy sleep and is generally considered normal and without any adverse effects.
7.1. The Impact of Nightmares
Nightmares are an exception to this rule. Because they involve awakenings, frequent nightmares can become problematic. Distressing dreams may cause a person to avoid sleep, leading to sleep deprivation. This can trigger a REM sleep rebound, which can exacerbate nightmares.
7.2. Seeking Professional Help
Individuals experiencing nightmares more than once a week, fragmented sleep, or daytime sleepiness or mood changes should consult with a doctor. A doctor can assess these symptoms to determine the potential causes and treatments for their sleeping problem.
8. How To Improve Dream Recall?
For those interested in documenting or interpreting their dreams, remembering them is essential. Dream recall ability varies among individuals and may change with age.
8.1. Tips for Improving Dream Recall
While there’s no foolproof method for improving dream recall, experts recommend these tips:
- Reflect Upon Waking: Upon waking up, immediately think about your dreams. Dreams can fade quickly, so make recalling them your top priority. Before sitting up or speaking to your bed partner, close your eyes and mentally replay your dreams.
- Keep a Dream Journal: Keep a journal or app handy to record your dream content. It’s essential to have a way to quickly capture dream details before they vanish, even if you wake up from a dream during the night. Many find a pen and paper on their nightstand effective, but smartphone apps are also available for creating an organized and searchable dream journal.
- Wake Up Peacefully: Try to wake up peacefully in the morning. An abrupt awakening, such as from an alarm clock, can jolt you awake and disrupt your dream recall.
- Prioritize Dream Recall: Before bedtime, remind yourself that you want to remember your dreams and repeat this mantra before going to sleep. While this alone can’t guarantee dream recall, it can encourage you to take the time to reflect on dreams before starting your day.
9. How To Deal With Nightmares?
People who experience frequent nightmares that disrupt sleep should consult with a doctor to determine if they have nightmare disorder or another condition impacting their sleep quality. Treatment for nightmare disorder often involves talk therapy to address negative thinking, stress, and anxiety that can worsen nightmares.
9.1. Therapeutic Approaches
Many types of talk therapy aim to alleviate worries or fears, including those triggered by nightmares. Exposure or desensitization therapy can help patients reframe their emotional response to negative imagery, as trying to suppress negative thoughts may actually intensify nightmares.
9.2. Improving Sleep Hygiene
Another approach to reducing nightmares involves improving sleep hygiene, which encompasses both sleep-related habits and the bedroom environment. Healthy sleep hygiene can promote more predictable and sound sleep, even in the presence of bad dreams. Examples of healthy sleep tips include:
- Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Stick to a consistent sleep schedule every day, even on weekends or days off.
- Select Pre-Bed Content Wisely: Avoid scary, distressing, or stimulating content in the hours before bed, as it can trigger negative thoughts during sleep.
- Wind Down Each Night: Regular exercise during the day can improve sleep quality. In the evening, allow your mind and body to relax calmly before bed with light stretching, deep breathing, or other relaxation techniques.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Alcohol can lead to more concentrated REM sleep later in the night, increasing the risk of nightmares. Caffeine is a stimulant that can disrupt your sleep schedule and keep your brain alert when you want to sleep.
- Minimize Bedroom Distractions: Create a sleep environment that is dark, quiet, smells pleasant, and has a comfortable temperature. A supportive mattress and pillow can enhance the comfort and coziness of your bed. All of these factors make it easier to feel calm and prevent unwanted awakenings that can disrupt sleep patterns.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Dreams
To further address common questions and concerns about dreams, here’s a comprehensive FAQ section:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Why do dreams happen? | Dreams are thought to occur due to brain activity during sleep, possibly for memory consolidation, emotional processing, or as a byproduct of brain function. |
| What is REM sleep and its relation to dreams? | REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep is a stage of sleep characterized by heightened brain activity and is most associated with vivid and intense dreaming. |
| Do all people dream? | Yes, everyone dreams, but not everyone remembers their dreams. Dream recall varies from person to person. |
| What are lucid dreams? | Lucid dreams are dreams in which the dreamer is aware that they are dreaming and may even be able to control the dream’s content. |
| Can dreams predict the future? | There’s no scientific evidence to support the idea that dreams can predict the future. Dreams are more likely reflections of past experiences and current concerns. |
| What causes nightmares? | Nightmares can be triggered by stress, anxiety, trauma, certain medications, or underlying sleep disorders. |
| How can I stop having nightmares? | Improving sleep hygiene, practicing relaxation techniques, and seeking therapy can help reduce the frequency of nightmares. |
| What does it mean if I keep having the same dream? | Recurring dreams may indicate unresolved issues or concerns in your waking life that your subconscious is trying to process. |
| Is there a scientific way to interpret dreams? | Dream interpretation is subjective, but some psychologists believe that dreams can provide insight into a person’s thoughts, emotions, and experiences. |
| When should I be concerned about my dreams? | If dreams are frequently disturbing, causing significant distress, or interfering with daytime functioning, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional or sleep specialist. |
| Can external factors influence our dreams? | Yes, external factors like sounds, smells, temperature, and physical sensations can influence the content and intensity of dreams. |
| How long do dreams typically last? | The duration of dreams can vary, but they are generally longer and more vivid during REM sleep, with some dreams lasting up to 30 minutes. |
| Why do we sometimes forget our dreams? | Dreams are often forgotten due to the brain’s state during sleep, which is not conducive to memory formation. Additionally, the content of dreams can be bizarre and difficult to encode into long-term memory. |
| Can meditation or mindfulness affect our dreams? | Yes, practicing meditation or mindfulness techniques can promote relaxation, reduce stress, and improve sleep quality, which may lead to more positive and memorable dream experiences. |
| Is it possible to influence or control our dreams? | While not always possible, techniques like lucid dreaming induction and dream incubation can help increase awareness and influence over dream content. |
| Can medications or substances affect our dreams? | Yes, certain medications, alcohol, and recreational drugs can alter sleep patterns and affect the frequency, intensity, and content of dreams, sometimes leading to vivid or disturbing dream experiences. |
| Are there cultural differences in dream interpretation? | Yes, dream interpretation varies across cultures, with different symbols, themes, and beliefs associated with specific dream elements. |
| Do animals dream? | Studies suggest that animals, particularly mammals and birds, experience brain activity patterns during sleep similar to those observed in humans, indicating that they may also dream. |
| What role does sleep deprivation play in our dreams? | Sleep deprivation can lead to more intense and vivid dreams, as the brain attempts to compensate for lost REM sleep during subsequent sleep periods. |
| Can physical conditions or illnesses affect our dreams? | Yes, certain physical conditions, such as fever, pain, or neurological disorders, can influence the content and intensity of dreams, sometimes resulting in more bizarre or unsettling dream experiences. |
| How can I create a dream journal to track my dreams? | To create a dream journal, keep a notebook or use a digital app to record dream details immediately upon waking, including the date, time, emotions, and any specific images, symbols, or events that you recall from the dream. |
| Can dreams help with problem-solving or creativity? | Some researchers believe that dreams can facilitate problem-solving and creativity by allowing the brain to explore alternative perspectives and make novel connections between ideas in a relaxed and imaginative state. |
| Are there any known benefits to lucid dreaming? | Lucid dreaming has been associated with potential benefits such as reducing nightmares, enhancing self-awareness, improving motor skills, and fostering creativity. |
| What is the relationship between dreams and mental health? | Dreams can reflect and influence mental health, with distressing or recurring dreams potentially indicative of underlying mental health issues, while positive or therapeutic dreams may contribute to emotional well-being. |
| Where can I find more information about sleep and dreams? | For more information about sleep and dreams, you can consult reputable sources such as sleep foundations, medical websites, scientific journals, and healthcare professionals specializing in sleep medicine. |
| How does WHY.EDU.VN enhance the understanding of dreams? | WHY.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive resource for exploring the science and psychology of dreams, offering expert insights, research findings, and practical tips for improving dream recall and managing dream-related concerns. |
| Does WHY.EDU.VN offer personalized guidance on dream interpretation? | While WHY.EDU.VN provides general information about dream interpretation, personalized guidance may require consultation with a qualified mental health professional or dream analyst who can consider individual experiences and contexts. |


Unlock the Secrets of Your Dreams with WHY.EDU.VN
Do you find yourself pondering the mysteries of your dreams? Are you seeking answers to the question of “why do dreams happen?” At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand the human desire to unravel the complexities of the sleeping mind.
We recognize the challenges in finding accurate and reliable answers to your questions. The internet is awash with information, but discerning credible sources can be daunting. Perhaps you’ve struggled to understand technical explanations or longed for a platform where you can ask questions and receive expert responses.
That’s why we created WHY.EDU.VN – a comprehensive resource dedicated to providing clear, evidence-based answers to your questions about dreams and a wide range of other topics. Our team of experts is committed to delivering detailed, easy-to-understand explanations, comparing diverse viewpoints, and ensuring the accuracy of our information.
Ready to delve deeper into the world of dreams?
Visit WHY.EDU.VN today to ask your questions and discover a wealth of knowledge from our team of experts. Let us help you unlock the secrets of your dreams and gain a better understanding of yourself. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (213) 555-0101. Start your journey of discovery at why.edu.vn today!