Why Does California Have So Many Fires? Understanding the causes of California wildfires is critical, and WHY.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing clear, expert-backed answers. The increasing frequency and intensity of these devastating events can be attributed to a combination of factors, including climate change, historical fire suppression policies, and expanding human development. To fully grasp the complexities, let’s delve into the environmental impacts, fire prevention strategies, and long-term solutions to mitigate the wildfire crisis.
1. Understanding the California Wildfire Crisis
California has experienced a surge in large, destructive wildfires in recent years. The increasing frequency and intensity of these fires have raised serious concerns about the state’s environment, economy, and public health. Several factors contribute to this crisis, creating a complex challenge that requires a multi-faceted approach.
1.1. Frequency and Intensity of Recent Wildfires
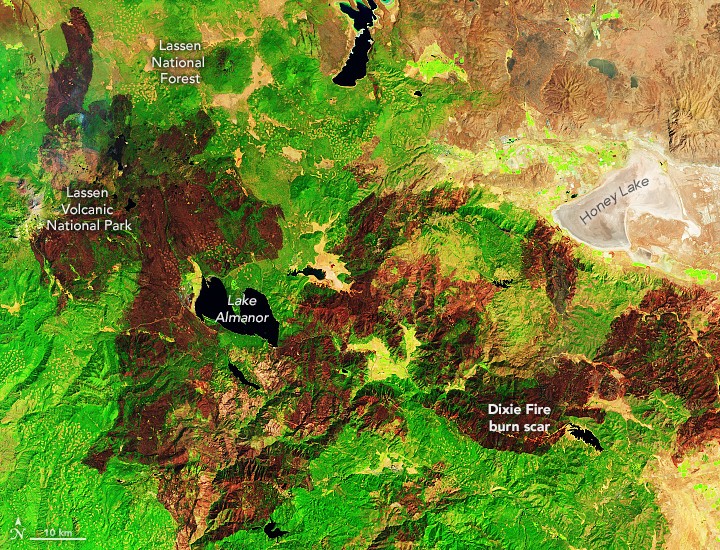
Eight of California’s ten largest fires on record, and twelve of the top twenty, have occurred within the past five years, according to the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (Cal Fire). These fires have collectively burned a significant portion of the state, equivalent to the size of Connecticut. The Dixie Fire in 2021 and the August Complex Fire in 2020 each burned nearly 1 million acres.
1.2. Impact on Structures and Lives
The destructive impact of these fires extends beyond the environment. Thirteen of California’s twenty most destructive wildfires have occurred in the past five years, destroying 40,000 homes, businesses, and infrastructure. These fires have also resulted in tragic loss of life, making them a pressing public safety issue.
1.3. Increasing Burned Area and Average Fire Size
The total area burned by fires each year and the average size of fires is increasing. Data from the Historic Fires Database shows that about 3 percent of the state’s land surfaces burned between 1970-1980, while from 2010-2020, it was 11 percent. This shift toward larger, more frequent fires is a clear indication of the escalating crisis.
2. Key Factors Contributing to California Wildfires
A confluence of factors drives the surge of large, destructive fires in California. These include climate change-induced drought and heat, overgrown forests due to fire suppression, and expanding human development along forest edges. Understanding these factors is essential for developing effective prevention and mitigation strategies.
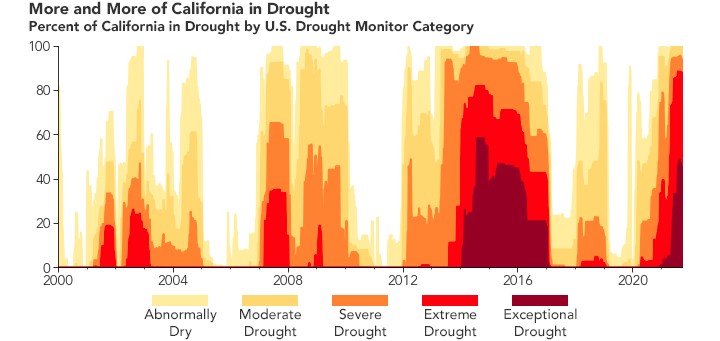
2.1. Climate Change and Extreme Drought Conditions
Climate change is exacerbating drought and heat conditions in California, making forests drier and more susceptible to fire. The current drought is unprecedented, with each of the past three decades experiencing substantially worse drought than any decade over the last 150 years. Drought weakens trees and plants, making them easier to burn, and adds vast amounts of dead wood to the landscape.
2.2. The Role of Dry Lightning Sieges
Extreme weather events, such as dry lightning sieges, can ignite thousands of fires in a single night. While not always the primary cause, these events can overwhelm firefighting resources and contribute to the rapid spread of wildfires.
2.3. Historical Fire Suppression and Forest Management
Decades of fire suppression have led to overgrown forests with an accumulation of dry vegetation, which serves as fuel for fires. This fuel buildup increases the intensity and spread of wildfires, making them more difficult to control.
2.4. Population Growth and Wildland-Urban Interface
Rapid population growth along the edges of forests, known as the wildland-urban interface (WUI), increases the risk of human-caused fires and puts more homes and infrastructure in harm’s way. This interface creates a complex challenge, as it requires balancing development with fire safety and prevention.
3. The Science Behind the Wildfires
Understanding the scientific principles behind wildfires is crucial for predicting and managing these events. This includes understanding how climate change influences fire behavior, the role of fuel moisture, and the impact of wind on fire spread.
3.1. How Heat Affects Fire Intensity
Heat essentially turns the atmosphere into a giant sponge that draws moisture from plants, making it possible for fires to burn hotter and longer. Meteorological data shows that recent years have been among the warmest on record in California, with temperatures significantly warmer than average.
3.2. The Relationship Between Temperature and Moisture
Air can absorb about 7 percent more water for every degree Celsius it warms. This means that warmer temperatures lead to drier vegetation, creating ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly.
3.3. Understanding Fuel Moisture and Fire Behavior
Fuel moisture is a critical factor in determining fire behavior. When vegetation is dry, it ignites more easily and burns more intensely. Climate change-induced drought reduces fuel moisture, increasing the risk of large, destructive wildfires.
4. NASA’s Role in Monitoring and Studying Wildfires
NASA plays a critical role in monitoring and studying wildfires using satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies. These tools provide valuable data on fire perimeters, burn severity, and vegetation health, helping scientists and firefighters better understand and manage wildfires.
4.1. Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing Technologies
Satellite imagery from Landsat 8 and other satellites provides detailed information on fire activity and its impact on the landscape. Remote sensing technologies allow scientists to monitor vegetation health and fuel moisture levels, helping them assess fire risk.
4.2. Data on Fire Perimeters and Burn Severity
NASA’s Earth Science Applied Sciences program collects and analyzes data on fire perimeters and burn severity. This data is used to track the spread of wildfires and assess the damage they cause to ecosystems and communities.
4.3. Collaboration with Other Agencies and Organizations
NASA collaborates with other agencies and organizations, such as the U.S. Geological Survey and the National Interagency Fire Center, to share data and expertise. This collaboration is essential for developing effective strategies for wildfire prevention and management.
5. Fire Management Strategies and Prevention Efforts
Effective fire management strategies and prevention efforts are essential for reducing the risk of wildfires and protecting communities. These strategies include fuel reduction, prescribed burns, and public education campaigns.
5.1. Fuel Reduction and Forest Thinning
Fuel reduction involves removing or modifying vegetation to reduce the amount of fuel available for fires. Forest thinning, a type of fuel reduction, involves selectively removing trees to reduce competition and increase the health of remaining trees.
5.2. The Use of Prescribed Burns
Prescribed burns are controlled fires that are intentionally set to reduce fuel buildup and restore ecosystems. These burns can help prevent large, destructive wildfires by reducing the amount of fuel available for them to burn.
5.3. Public Education and Fire Safety
Public education campaigns are essential for raising awareness about fire safety and preventing human-caused fires. These campaigns can teach people how to properly dispose of cigarettes, use fireworks safely, and maintain their properties to reduce fire risk.
6. The Economic Impact of California Wildfires
California wildfires have a significant economic impact, costing billions of dollars in damages, firefighting expenses, and lost productivity. Understanding these costs is essential for justifying investments in fire prevention and mitigation strategies.
6.1. Costs of Fire Suppression and Damage
The costs of fire suppression and damage from wildfires can be enormous. Firefighting expenses can reach hundreds of millions of dollars for a single fire, and the cost of repairing or replacing damaged infrastructure can be even higher.
6.2. Impact on Agriculture and Tourism
Wildfires can have a devastating impact on agriculture and tourism, two important sectors of California’s economy. Smoke from wildfires can damage crops and reduce yields, and the fires themselves can destroy vineyards, orchards, and other agricultural operations. Wildfires can also deter tourists from visiting affected areas, reducing revenue for hotels, restaurants, and other businesses.
6.3. Long-Term Economic Consequences
The long-term economic consequences of wildfires can be significant. Wildfires can lead to job losses, reduced property values, and increased insurance rates. They can also damage ecosystems and reduce the availability of natural resources, such as timber and water.
7. The Social and Health Impacts of Wildfires
Wildfires have significant social and health impacts, affecting the physical and mental well-being of individuals and communities. Smoke from wildfires can cause respiratory problems, and the stress of evacuation and displacement can lead to mental health issues.
7.1. Air Quality and Respiratory Health
Smoke from wildfires can contain harmful pollutants that can cause respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis. Exposure to wildfire smoke can also increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
7.2. Mental Health and Displacement
The stress of evacuation and displacement can lead to mental health issues, such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Wildfires can also disrupt social networks and support systems, making it more difficult for people to cope with the aftermath of the fires.
7.3. Impact on Vulnerable Populations
Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, children, and low-income communities, are disproportionately affected by wildfires. These populations may have limited resources to prepare for and recover from wildfires, and they may be more susceptible to the health impacts of wildfire smoke.
8. Future Projections and Long-Term Solutions
Future projections suggest that California wildfires will continue to increase in frequency and intensity unless significant action is taken to address the underlying causes. Long-term solutions include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving forest management practices, and building more resilient communities.
8.1. Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is essential for mitigating climate change and reducing the risk of wildfires. Adaptation measures, such as building more fire-resistant homes and creating defensible space around properties, can help communities better prepare for and withstand wildfires.
8.2. Sustainable Forest Management Practices
Sustainable forest management practices can help reduce fuel buildup and improve the health of forests. These practices include thinning, prescribed burns, and reforestation with fire-resistant species.
8.3. Community Resilience and Preparedness
Building community resilience and preparedness is essential for helping communities recover from wildfires. This includes developing evacuation plans, creating emergency shelters, and providing support services to those affected by the fires.
9. Case Studies of Recent California Wildfires
Examining case studies of recent California wildfires can provide valuable insights into the causes and consequences of these events. These case studies can also highlight best practices for wildfire prevention and management.
9.1. The Dixie Fire (2021)
The Dixie Fire, which burned nearly 1 million acres in 2021, was one of the largest wildfires in California history. The fire was caused by a tree falling on a power line and was fueled by dry vegetation and strong winds.
9.2. The August Complex Fire (2020)
The August Complex Fire, which burned over 1 million acres in 2020, was the largest wildfire in California history. The fire was caused by a series of lightning strikes and was fueled by dry vegetation and hot, dry weather.
9.3. The Camp Fire (2018)
The Camp Fire, which destroyed the town of Paradise in 2018, was the deadliest and most destructive wildfire in California history. The fire was caused by a faulty power line and was fueled by dry vegetation and strong winds.
10. Expert Opinions on Wildfire Trends
Experts agree that California wildfires are likely to continue to increase in frequency and intensity unless significant action is taken to address the underlying causes. These experts emphasize the need for a multi-faceted approach that includes climate change mitigation, forest management, and community preparedness.
10.1. Quotes from Fire Scientists and Climatologists
Fire scientists and climatologists have warned about the increasing risk of wildfires in California for many years. They emphasize the need for urgent action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve forest management practices.
10.2. Recommendations for Policy Changes and Prevention Measures
Experts recommend a range of policy changes and prevention measures to reduce the risk of wildfires. These include investing in fuel reduction projects, increasing funding for fire prevention and suppression, and implementing stricter building codes in the wildland-urban interface.
10.3. Future Outlook for Wildfire Management
The future outlook for wildfire management in California is challenging. However, with a concerted effort to address the underlying causes of the problem, it is possible to reduce the risk of wildfires and protect communities from their devastating impacts.
California’s devastating wildfires stem from a mix of climate change, overgrown forests, and human encroachment. Understanding these factors and implementing effective management strategies are crucial.
[Image of Dixie Fire Burn Scar from Landsat 8]
Table: Key Factors Contributing to California Wildfires
| Factor | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change | Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and extreme weather events | Drier vegetation, increased fire risk, longer fire seasons |
| Fire Suppression | Decades of suppressing natural fires leading to fuel buildup | Increased fire intensity and spread, larger and more destructive fires |
| Population Growth | Expansion of communities into wildland areas (wildland-urban interface) | Increased risk of human-caused ignitions, greater exposure of homes and infrastructure to fire |
| Forest Management | Inadequate forest management practices resulting in dense, unhealthy forests | Increased fuel loads, higher tree mortality, greater susceptibility to fire |
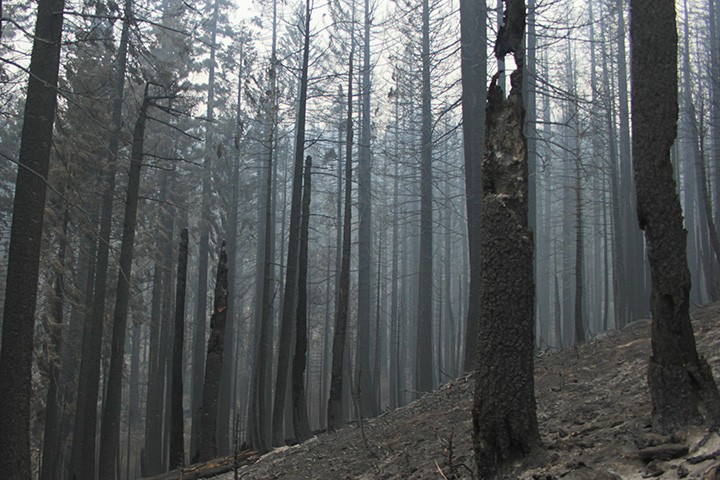

[Image of Charred Forests in Plumas National Forest]
List: Effective Fire Management Strategies
- Fuel Reduction: Removing excess vegetation through thinning and prescribed burns.
- Early Detection: Utilizing advanced technology for rapid fire detection and response.
- Community Education: Raising awareness among residents about fire prevention and preparedness.
[Image of California Drought Monitor]
FAQ Section: California Wildfires
- What are the primary causes of wildfires in California? Climate change, overgrown forests, and human activity.
- How does climate change contribute to wildfires? It leads to drier conditions and longer fire seasons.
- What is the wildland-urban interface? The area where homes and wildland vegetation meet, increasing fire risk.
- What are prescribed burns? Controlled fires used to reduce fuel buildup and prevent larger fires.
- How can communities prepare for wildfires? By creating defensible space, developing evacuation plans, and staying informed.
- What role does NASA play in monitoring wildfires? NASA uses satellites to track fire activity and assess environmental damage.
- How does drought impact wildfires? It dries out vegetation, making it easier to ignite and spread fires.
- What is fuel reduction? Removing vegetation to decrease the amount of flammable material available.
- How do dry lightning sieges contribute to wildfires? They can ignite numerous fires simultaneously, overwhelming resources.
- What are the long-term solutions to mitigate wildfires? Climate change mitigation, forest management, and community resilience.
Contact Information:
For further inquiries or to learn more about wildfire prevention and safety, please contact us:
Address: 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101
Website: WHY.EDU.VN
Are you seeking in-depth answers to complex questions? Do you need reliable, expert-backed information? Visit why.edu.vn today to ask your questions and discover a wealth of knowledge. Our team of specialists is ready to provide the insights you need.
The information provided here is from credible sources, including NASA, Cal Fire, and the U.S. Geological Survey.