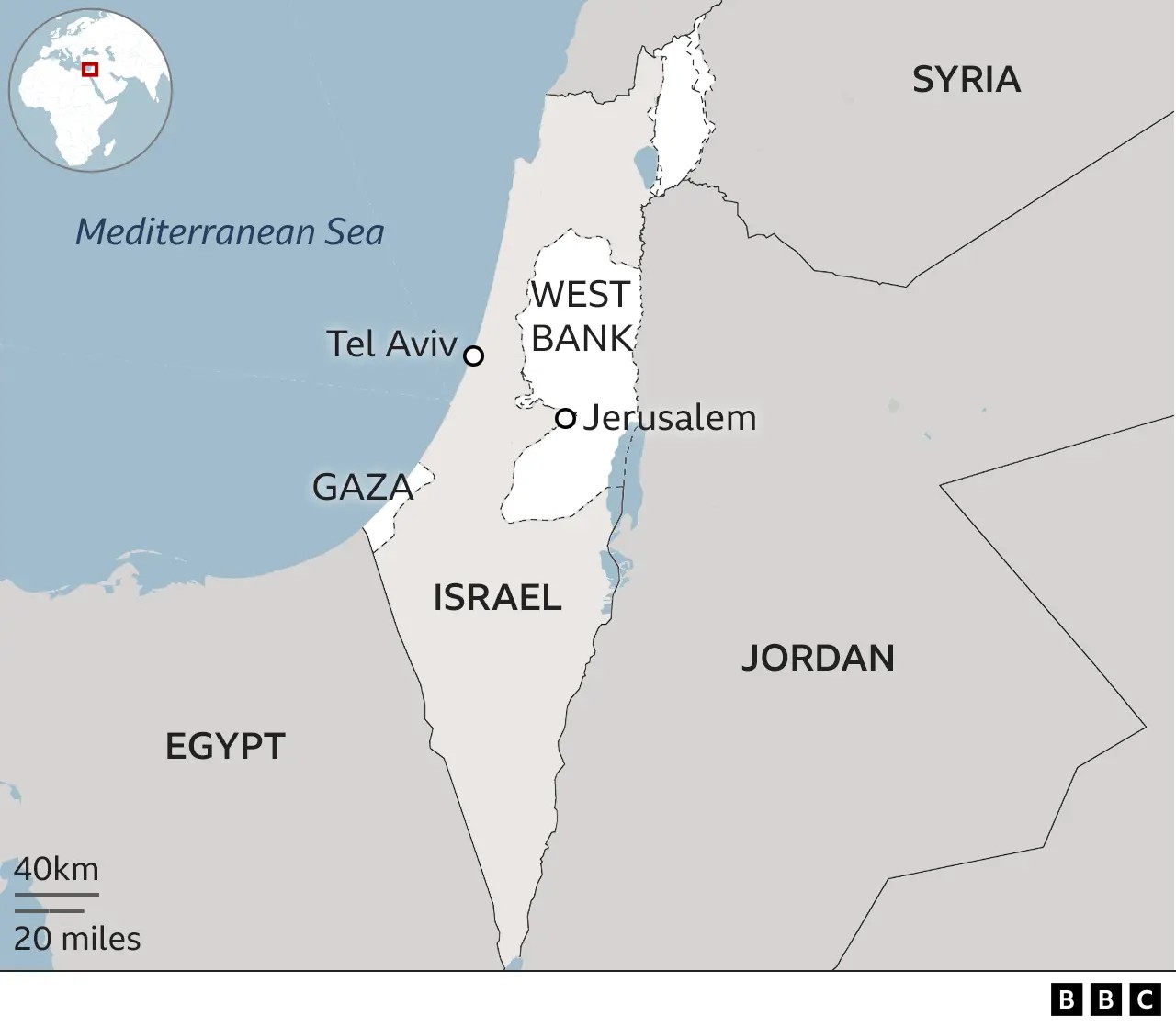
Why Are Israel And Hamas Fighting is a complex question with deep historical roots. This comprehensive analysis from WHY.EDU.VN explores the reasons behind the ongoing conflict, the key players involved, and the potential paths toward resolution. Delve into the intricate dynamics of this volatile situation to gain a clear understanding of the geopolitical landscape, the humanitarian crisis, and the search for lasting peace, utilizing expert insights, providing diverse viewpoints, and including regional stability.
1. The Genesis of the Conflict: Historical Roots
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a protracted struggle with roots stretching back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Understanding the history of this conflict is crucial to understanding why are Israel and Hamas fighting.
1.1. Zionism and Palestinian Nationalism
Zionism, the movement for Jewish self-determination and the establishment of a Jewish state in Palestine, emerged in the late 19th century. Simultaneously, Palestinian nationalism developed among the Arab population of Palestine, who sought self-determination and independence.
1.2. The British Mandate and Competing Claims
Following World War I, the League of Nations granted Britain a mandate over Palestine. The British Mandate period (1920-1948) saw increasing Jewish immigration to Palestine, leading to tensions and clashes with the Arab population. Both groups laid claim to the same territory, resulting in escalating conflict.
1.3. The 1947 UN Partition Plan
In 1947, the United Nations proposed a plan to partition Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states, with Jerusalem under international control. The Jewish leadership accepted the plan, while the Arab leadership rejected it.
1.4. The 1948 Arab-Israeli War and its Aftermath
Following the expiration of the British Mandate in May 1948, Israel declared its independence. The Arab states launched a war against Israel, which resulted in an Israeli victory. The war led to the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians, known as the Nakba (catastrophe), and the establishment of Israel within expanded borders. This event remains a central point of contention and a major factor contributing to why are Israel and Hamas fighting.
2. The Rise of Hamas: Ideology, Objectives, and Strategies
Hamas, an acronym for “Harakat al-Muqawama al-Islamiyya” (Islamic Resistance Movement), emerged in 1987 during the First Intifada, a Palestinian uprising against Israeli occupation.
2.1. Ideological Foundations
Hamas’s ideology is rooted in Islamic fundamentalism. The group’s charter calls for the establishment of an Islamic state in all of historical Palestine, rejecting the existence of Israel. It views armed resistance as a legitimate means to achieve its goals.
2.2. Political and Social Activities
In addition to its armed wing, Hamas operates a network of social and charitable organizations that provide services to the Palestinian population in Gaza. This has enabled the group to gain popular support and legitimacy among Palestinians.
2.3. Armed Resistance and Terrorism
Hamas has engaged in armed resistance against Israel, including suicide bombings, rocket attacks, and other acts of violence. These actions have been condemned internationally as terrorism. According to the U.S. State Department, Hamas has been responsible for numerous terrorist attacks, resulting in the deaths of hundreds of civilians.
2.4. Control of the Gaza Strip
In 2006, Hamas won a majority in the Palestinian legislative elections. Following a conflict with the rival Fatah faction in 2007, Hamas took control of the Gaza Strip, leading to an Israeli blockade of the territory.
3. Key Events and Escalations: A Timeline of Conflict
The conflict between Israel and Hamas has been punctuated by several major escalations and periods of intense violence.
3.1. The First and Second Intifadas
The First Intifada (1987-1993) and the Second Intifada (2000-2005) were Palestinian uprisings against Israeli occupation. These uprisings were marked by clashes, protests, and acts of violence on both sides.
3.2. Operation Cast Lead (2008-2009)
In December 2008, Israel launched Operation Cast Lead in response to Hamas rocket attacks from Gaza. The operation resulted in widespread destruction and casualties in Gaza. A UN report found evidence of war crimes committed by both sides during the conflict.
3.3. Operation Pillar of Defense (2012)
In November 2012, Israel launched Operation Pillar of Defense in response to renewed Hamas rocket attacks. The operation lasted for eight days and resulted in further casualties and damage in Gaza.
3.4. Operation Protective Edge (2014)
In July 2014, Israel launched Operation Protective Edge following a surge in rocket fire from Gaza. The operation lasted for 50 days and resulted in the deaths of over 2,200 Palestinians and 73 Israelis. The conflict drew widespread international condemnation due to the high number of civilian casualties. The actions during Operation Protective Edge significantly contributed to why are Israel and Hamas fighting.
3.5. The 2021 Israel-Gaza Crisis
In May 2021, tensions escalated in Jerusalem over planned evictions of Palestinian families from their homes in Sheikh Jarrah and restrictions on access to the Al-Aqsa Mosque. Hamas launched rocket attacks against Israel, leading to Israeli airstrikes in Gaza. The conflict lasted for 11 days and resulted in over 250 deaths in Gaza and 13 deaths in Israel.
4. The Geopolitical Context: Regional and International Factors
The conflict between Israel and Hamas is influenced by a complex web of regional and international factors.
4.1. Regional Powers and Alliances
Several regional powers, including Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Qatar, have played a role in the conflict, often supporting different sides. Iran has been a key supporter of Hamas, providing funding, training, and weapons.
4.2. The Role of the United States
The United States has been a strong ally of Israel and has provided significant military and economic assistance. The U.S. has also played a role in mediating peace negotiations between Israel and the Palestinians. According to a report by the Congressional Research Service, the U.S. has provided Israel with over $3 billion in annual military aid.
4.3. International Law and Human Rights
International law and human rights organizations have played a role in monitoring and reporting on the conflict. Organizations such as Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch have documented alleged war crimes and human rights abuses committed by both sides.
4.4. The Israeli-Palestinian Peace Process
The Israeli-Palestinian peace process has been stalled for many years. Several attempts to reach a two-state solution have failed due to disagreements over key issues such as borders, settlements, and the status of Jerusalem. The failure of the peace process has contributed to the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas.
5. Why Are Israel and Hamas Fighting: Core Grievances and Motivations
To understand why are Israel and Hamas fighting, it is essential to examine the core grievances and motivations of both sides.
5.1. Palestinian Grievances
Palestinians have several long-standing grievances, including the ongoing Israeli occupation of the West Bank and Gaza, the expansion of Israeli settlements, the blockade of Gaza, and the denial of their right to self-determination. These grievances have fueled Palestinian anger and resentment, contributing to the conflict.
5.2. Hamas’s Motivations
Hamas is driven by its ideological commitment to establishing an Islamic state in all of historical Palestine and its opposition to the existence of Israel. The group also seeks to liberate Palestinian prisoners held in Israeli jails and to end the blockade of Gaza. These motivations have driven Hamas to engage in armed resistance against Israel.
5.3. Israeli Security Concerns
Israel views Hamas as a terrorist organization that poses a significant security threat. Israel has repeatedly stated that it has a right to defend itself against Hamas rocket attacks and other acts of violence. Israel also seeks to maintain control over Jerusalem and to protect its borders.
5.4. Mutual Distrust and Lack of Confidence
The conflict between Israel and Hamas is characterized by a deep-seated mutual distrust and lack of confidence. Both sides view the other as an existential threat and are unwilling to make concessions. This has made it difficult to reach a lasting peace agreement.
6. The Impact on Civilians: Humanitarian Crisis in Gaza
The conflict between Israel and Hamas has had a devastating impact on civilians, particularly in the Gaza Strip.
6.1. Casualties and Displacement
The repeated rounds of fighting have resulted in thousands of deaths and injuries, the majority of whom have been Palestinian civilians. The conflicts have also led to widespread displacement, with hundreds of thousands of Palestinians forced to flee their homes.
6.2. Economic Hardship and Poverty
The Israeli blockade of Gaza has severely restricted the movement of goods and people, leading to economic hardship and poverty. The UN estimates that over 80% of the population in Gaza relies on humanitarian assistance to survive.
6.3. Psychological Trauma
The constant violence and insecurity have taken a heavy toll on the mental health of civilians in Gaza. Many Palestinians suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other psychological problems. According to a study by the Gaza Community Mental Health Programme, over 50% of children in Gaza exhibit symptoms of PTSD.
6.4. Damage to Infrastructure
The conflicts have caused widespread damage to infrastructure in Gaza, including homes, schools, hospitals, and power plants. This has further exacerbated the humanitarian crisis and made it difficult for people to access basic services.
7. Obstacles to Peace: Key Issues and Challenges
Several key issues and challenges stand in the way of a lasting peace agreement between Israel and Hamas.
7.1. The Status of Jerusalem
Both Israel and the Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their capital. Israel considers Jerusalem its “united and eternal capital,” while the Palestinians want East Jerusalem to be the capital of a future Palestinian state.
7.2. Israeli Settlements
The expansion of Israeli settlements in the West Bank is a major obstacle to peace. The settlements are considered illegal under international law and are viewed by Palestinians as a barrier to the creation of a viable Palestinian state.
7.3. The Right of Return for Palestinian Refugees
Palestinian refugees demand the right to return to their former homes in Israel. Israel rejects this demand, arguing that it would threaten the Jewish character of the state.
7.4. Security Concerns
Israel insists on maintaining security control over the West Bank and Gaza to prevent attacks by Hamas and other militant groups. The Palestinians want full sovereignty over their territory.
7.5. Disunity Among Palestinians
The division between Hamas and Fatah has weakened the Palestinian position and made it difficult to negotiate a unified peace agreement with Israel.
8. Potential Solutions and Pathways to Peace
Despite the obstacles, there are potential solutions and pathways to peace between Israel and Hamas.
8.1. A Two-State Solution
The two-state solution, which envisions the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel, remains the most widely supported framework for resolving the conflict. However, significant compromises and concessions would be required from both sides to reach an agreement.
8.2. International Mediation and Support
International mediation and support are crucial to facilitating peace negotiations between Israel and Hamas. The United States, the European Union, and other international actors can play a role in encouraging both sides to make concessions and to reach a lasting peace agreement.
8.3. Economic Development and Humanitarian Assistance
Economic development and humanitarian assistance can help to improve the living conditions of Palestinians in Gaza and to create a more stable environment for peace. International donors can provide funding for infrastructure projects, job creation programs, and other initiatives to support the Palestinian economy.
8.4. Confidence-Building Measures
Confidence-building measures, such as prisoner releases, easing of the blockade of Gaza, and increased cooperation on security matters, can help to improve relations between Israel and Hamas and to create a more conducive environment for peace negotiations.
8.5. Grassroots Initiatives and People-to-People Dialogue
Grassroots initiatives and people-to-people dialogue can help to promote understanding and empathy between Israelis and Palestinians. These initiatives can bring people from both sides together to share their experiences, to learn about each other’s perspectives, and to build relationships.
9. Examining Recent Developments
Staying abreast of the most recent developments is crucial to comprehending why are Israel and Hamas fighting and to anticipate future trajectories.
9.1. Current Ceasefire Efforts
As of late 2024 and early 2025, international mediators continue to push for a durable ceasefire agreement between Israel and Hamas. These efforts often involve complex negotiations over hostage releases, humanitarian aid, and the easing of restrictions on Gaza.
9.2. Shifting Regional Dynamics
The broader geopolitical landscape in the Middle East is constantly evolving. Normalisation agreements between Israel and some Arab states have altered regional alliances and may influence future peace prospects.
9.3. Humanitarian Aid Initiatives
Various international organisations are working to provide essential aid to Gaza’s population, including food, medical supplies, and shelter. The effectiveness and sustainability of these initiatives remain critical to mitigating the humanitarian crisis.
10. Addressing Misconceptions and Biases
It’s important to address common misconceptions and biases that can cloud understanding of the conflict:
10.1. The Myth of Unilateral Blame
Attributing blame to only one side oversimplifies a complex historical and political reality. Both Israelis and Palestinians have legitimate grievances and have experienced violence and displacement.
10.2. Equating Hamas with All Palestinians
Hamas does not represent all Palestinians. Many Palestinians do not support Hamas’s ideology or methods and seek a peaceful resolution to the conflict.
10.3. Ignoring the Impact of Occupation
The ongoing Israeli occupation of Palestinian territories significantly impacts Palestinian lives and fuels resentment, playing a crucial role in perpetuating the conflict.
FAQ: Understanding the Israel-Hamas Conflict
Here are some frequently asked questions about the conflict between Israel and Hamas:
1. What is Hamas?
Hamas is a Palestinian Islamist organization that governs the Gaza Strip. It has both a political and military wing.
2. What are Hamas’s goals?
Hamas seeks to establish an Islamic state in all of historical Palestine and opposes the existence of Israel.
3. Why does Hamas fire rockets into Israel?
Hamas says it fires rockets in response to Israeli occupation, the blockade of Gaza, and other grievances.
4. Why does Israel blockade Gaza?
Israel says the blockade is necessary to prevent Hamas from importing weapons and materials that could be used for attacks.
5. What is the humanitarian situation in Gaza?
The humanitarian situation in Gaza is dire, with high rates of poverty, unemployment, and food insecurity.
6. What is the two-state solution?
The two-state solution envisions the creation of an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel.
7. Why has the peace process failed?
The peace process has failed due to disagreements over key issues such as borders, settlements, and the status of Jerusalem.
8. What is the role of the United States in the conflict?
The United States has been a strong ally of Israel and has played a role in mediating peace negotiations.
9. What is the role of international law in the conflict?
International law provides a framework for addressing issues such as occupation, human rights, and the use of force.
10. What can be done to promote peace?
Potential solutions include a two-state solution, international mediation, economic development, and confidence-building measures.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities
Why are Israel and Hamas fighting is a question that demands a nuanced and comprehensive understanding of historical, political, and ideological factors. The conflict is deeply rooted in competing claims to land, mutual distrust, and a history of violence. Addressing the core grievances of both sides, promoting economic development, and fostering dialogue are essential steps toward building a more peaceful future.
For more in-depth analysis, diverse perspectives, and expert insights into this complex issue, visit WHY.EDU.VN. We provide a platform for exploring multifaceted topics and encourage informed discussions. Our commitment to providing accurate and reliable information empowers you to form your own well-reasoned conclusions.
Do you have more questions about the Israel-Hamas conflict or other complex issues?
Visit WHY.EDU.VN today! Our team of experts is ready to provide you with clear, concise answers and in-depth analysis. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101. Website: WHY.EDU.VN. Get the answers you need and expand your understanding of the world around you. Let why.edu.vn be your trusted source for knowledge and exploration.