Why Do I Get Bumps On My Tongue? Discover the potential causes, from minor irritations to underlying conditions. WHY.EDU.VN provides expert insights and solutions for managing tongue bumps and ensuring your oral health with the help of experienced experts and cutting-edge research, giving you peace of mind and a clearer path to recovery. Consider causes such as taste bud irritation, oral infections, and vitamin deficiencies.
1. Decoding Tongue Bumps: Common Causes and Solutions
Bumps on the tongue are a common concern, often causing discomfort and raising questions about their origin. These bumps can vary in size, shape, and color, and may be accompanied by pain or other symptoms. Understanding the potential causes of tongue bumps is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Let’s explore the most common reasons why you might find these unexpected guests on your tongue.
2. Irritated Taste Buds: A Frequent Culprit
Taste buds are small sensory organs on your tongue that allow you to experience different flavors. They are sensitive and can become irritated by various factors, leading to the development of bumps.
2.1. What Triggers Taste Bud Irritation?
- Hot Foods and Beverages: Consuming extremely hot foods or drinks can burn and irritate the taste buds, causing them to swell and become noticeable.
- Acidic Foods: Highly acidic foods like citrus fruits, tomatoes, and vinegar can also irritate the taste buds, leading to inflammation and bumps.
- Spicy Foods: The capsaicin in spicy foods can stimulate and sometimes irritate taste buds, especially if you’re not used to eating spicy foods regularly.
- Physical Trauma: Accidentally biting your tongue or scraping it against your teeth can injure the taste buds, resulting in temporary bumps.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to a buildup of bacteria and debris on the tongue, irritating the taste buds.
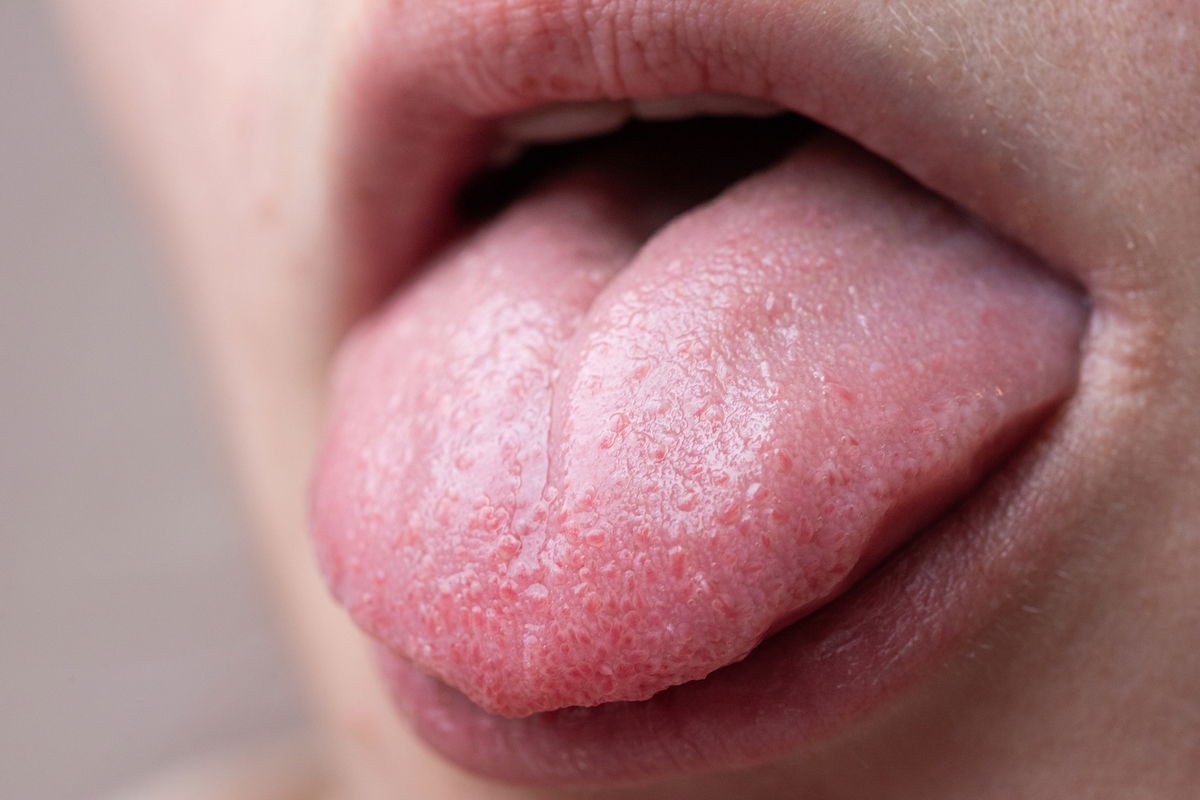 Irritated Taste Buds
Irritated Taste Buds
2.2. How to Soothe Irritated Taste Buds
- Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of hot, acidic, and spicy foods until your taste buds have healed.
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth gently, paying attention to your tongue, and floss regularly.
- Rinse with Warm Salt Water: Saltwater rinses can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water keeps your mouth moist and aids in the recovery process.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: If the bumps are painful, consider taking an over-the-counter pain reliever like ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
3. Infections: When Bumps Signal a Deeper Issue
Infections can also cause bumps to appear on the tongue. These infections can be bacterial, viral, or fungal in nature.
3.1. Common Oral Infections
- Oral Thrush (Candidiasis): A fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida yeast in the mouth. It appears as white, cottage cheese-like patches on the tongue and inner cheeks.
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV-1): This virus can cause cold sores on the lips and, less commonly, on the tongue. These sores start as small blisters that eventually rupture and form ulcers.
- Syphilis: A sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can cause painless sores called chancres to develop on the tongue or other areas of the mouth.
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease: A common viral infection, particularly in children, that causes sores in the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet.
3.2. Seeking Treatment for Oral Infections
If you suspect you have an oral infection, it’s essential to seek medical attention. A doctor or dentist can diagnose the infection and recommend the appropriate treatment.
- Antifungal Medications: For oral thrush, antifungal medications like nystatin or fluconazole may be prescribed.
- Antiviral Medications: For herpes simplex virus, antiviral medications like acyclovir or valacyclovir can help reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks.
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections like syphilis, antibiotics like penicillin are typically used.
4. Canker Sores: Small but Painful Ulcers
Canker sores are small, shallow ulcers that can appear on the tongue, inside the cheeks, or on the gums. While the exact cause of canker sores is unknown, several factors are believed to contribute to their development.
4.1. Potential Causes of Canker Sores
- Mouth Injury: Minor injuries to the mouth, such as biting your tongue or brushing too hard, can trigger canker sores.
- Stress: Emotional stress can weaken the immune system and make you more susceptible to canker sores.
- Food Sensitivities: Certain foods, such as chocolate, coffee, nuts, and acidic fruits, may trigger canker sores in some people.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during menstruation, can increase the risk of canker sores.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin B12, folate, and iron, may contribute to canker sores.
4.2. Managing Canker Sores
- Over-the-Counter Treatments: Topical creams and mouthwashes containing benzocaine or hydrogen peroxide can help relieve pain and promote healing.
- Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of foods and beverages that can irritate the sores, such as acidic or spicy foods.
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth gently and floss regularly to prevent infection.
- Saltwater Rinses: Rinse your mouth with warm salt water several times a day to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Prescription Medications: In severe cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger medications, such as corticosteroids.
5. Transient Lingual Papillitis: A Temporary Annoyance
Transient lingual papillitis (TLP), also known as “lie bumps,” is a common condition characterized by small, painful bumps on the tongue. These bumps are typically red or white and can cause a burning or tingling sensation.
5.1. What Causes TLP?
The exact cause of TLP is unknown, but several factors are thought to contribute to its development.
- Stress: Emotional stress can weaken the immune system and make you more susceptible to TLP.
- Food Irritation: Certain foods, such as acidic or spicy foods, may irritate the tongue and trigger TLP.
- Trauma: Minor injuries to the tongue, such as biting it or scraping it against your teeth, can cause TLP.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during menstruation, may increase the risk of TLP.
5.2. Treating TLP
TLP is usually a self-limiting condition, meaning it resolves on its own without treatment. However, there are several things you can do to relieve the discomfort associated with TLP.
- Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of foods and beverages that can irritate the tongue, such as acidic or spicy foods.
- Saltwater Rinses: Rinse your mouth with warm salt water several times a day to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: If the bumps are painful, consider taking an over-the-counter pain reliever like ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Topical Anesthetics: Apply a topical anesthetic, such as benzocaine, to the bumps to numb the area and relieve pain.
6. Allergic Reactions: An Unexpected Trigger
Allergic reactions to certain foods, medications, or other substances can sometimes manifest as bumps on the tongue. These bumps may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
6.1. Identifying Allergens
If you suspect you’re having an allergic reaction, it’s important to identify the allergen so you can avoid it in the future. Common allergens include:
- Foods: Nuts, shellfish, milk, eggs, soy, and wheat are common food allergens.
- Medications: Penicillin and other antibiotics are common medication allergens.
- Latex: Latex is a common allergen found in gloves, condoms, and other medical devices.
- Insect Stings: Bee stings and other insect stings can cause allergic reactions.
6.2. Managing Allergic Reactions
If you experience an allergic reaction, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. Mild allergic reactions can be treated with antihistamines, while severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) require epinephrine.
7. Oral Cancer: A Serious Concern
In rare cases, bumps on the tongue can be a sign of oral cancer. Oral cancer can develop on any part of the mouth, including the tongue, lips, gums, and inner cheeks.
7.1. Symptoms of Oral Cancer
- A sore or ulcer that doesn’t heal
- A lump or thickening in the mouth
- Red or white patches in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Numbness or pain in the mouth
7.2. Seeking Medical Attention
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor or dentist immediately. Early detection and treatment of oral cancer can significantly improve the chances of survival.
8. Other Potential Causes of Tongue Bumps
In addition to the causes listed above, there are several other potential causes of tongue bumps.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Deficiencies in certain vitamins, such as vitamin B12 and iron, can cause bumps on the tongue.
- Geographic Tongue: A harmless condition that causes smooth, red patches to develop on the tongue.
- Fissured Tongue: A condition characterized by deep grooves or fissures on the tongue.
- Benign Tumors: Non-cancerous growths that can develop on the tongue.
9. Expert Insights from WHY.EDU.VN
At WHY.EDU.VN, we understand that finding accurate and reliable information about your health concerns is essential. That’s why we’ve gathered a team of experienced medical professionals to provide you with expert insights and guidance.
9.1. Our Commitment to Accuracy
We are committed to providing you with accurate, up-to-date information that is based on scientific evidence. Our articles are thoroughly reviewed by medical experts to ensure their accuracy and completeness.
9.2. Personalized Answers to Your Questions
We also offer a platform where you can ask questions and receive personalized answers from our team of experts. Whether you’re concerned about a specific symptom or simply want to learn more about a particular health condition, we’re here to help.
10. When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of tongue bumps are harmless and resolve on their own, there are certain situations where you should seek medical attention.
- The bumps are painful or don’t heal after a few weeks.
- The bumps are accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, difficulty swallowing, or swollen lymph nodes.
- The bumps are growing or changing in appearance.
- You suspect you have an infection or an allergic reaction.
11. Take Control of Your Oral Health
Bumps on the tongue can be a nuisance, but understanding their potential causes can help you take control of your oral health. By practicing good oral hygiene, avoiding irritants, and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can keep your tongue healthy and bump-free.
12. Prevention Tips to Minimize Tongue Bumps
Preventing tongue bumps involves adopting healthy habits that promote oral hygiene and overall well-being. Here are some practical tips to help minimize the occurrence of tongue bumps:
12.1. Maintain Excellent Oral Hygiene
- Brush Regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss Daily: Floss between your teeth once a day to remove plaque and food particles.
- Clean Your Tongue: Gently brush your tongue or use a tongue scraper to remove bacteria and debris.
- Use Mouthwash: Rinse your mouth with an antibacterial mouthwash to kill germs and freshen your breath.
12.2. Watch Your Diet
- Limit Acidic Foods: Reduce your intake of acidic foods like citrus fruits, tomatoes, and vinegar.
- Avoid Spicy Foods: If you’re prone to tongue bumps, limit your consumption of spicy foods.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your mouth moist and prevent dryness.
12.3. Avoid Irritants
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can irritate the tongue and increase the risk of oral cancer.
- Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can also irritate the tongue.
- Avoid Hot Foods and Beverages: Let hot foods and beverages cool down before consuming them.
12.4. Manage Stress
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Engage in activities that help you relax, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to boost your immune system.
12.5. Regular Dental Checkups
- Visit Your Dentist: Schedule regular dental checkups to detect and treat any oral health problems early.
13. The Role of Diet in Tongue Health
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of your tongue and preventing bumps. Certain nutrients are essential for the proper function of the taste buds and the overall health of the oral mucosa.
13.1. Essential Nutrients for Tongue Health
- Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 is important for cell growth and repair. A deficiency can lead to glossitis, an inflammation of the tongue.
- Iron: Iron is necessary for the production of red blood cells. An iron deficiency can cause the tongue to become pale and smooth.
- Folate: Folate is another B vitamin that is essential for cell growth and repair. A deficiency can cause glossitis and canker sores.
- Zinc: Zinc is important for immune function and wound healing. A zinc deficiency can impair taste and increase the risk of oral infections.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps protect the body against damage from free radicals. A vitamin C deficiency can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of oral infections.
13.2. Foods That Promote Tongue Health
- Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and oral health.
- Lean Protein: Lean protein sources like chicken, fish, and beans provide essential amino acids for cell growth and repair.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like brown rice and oats are good sources of B vitamins and fiber.
- Dairy Products: Dairy products like milk and yogurt are rich in calcium and vitamin D, which are important for bone health.
14. The Psychological Impact of Tongue Bumps
Tongue bumps can have a significant psychological impact on individuals, especially if they are chronic or painful. The discomfort and appearance of tongue bumps can lead to anxiety, stress, and self-consciousness.
14.1. Addressing Psychological Concerns
- Acknowledge Your Feelings: Recognize and validate your feelings of anxiety, stress, or self-consciousness.
- Seek Support: Talk to a trusted friend, family member, or therapist about your concerns.
- Focus on What You Can Control: Take steps to manage your oral health and prevent future outbreaks.
- Practice Self-Care: Engage in activities that help you relax and reduce stress, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time with loved ones.
- Challenge Negative Thoughts: Replace negative thoughts with positive and realistic ones.
15. Innovations in Tongue Bump Treatment
The field of oral health is constantly evolving, with new innovations in the treatment of tongue bumps emerging regularly. These advancements offer hope for more effective and less invasive ways to manage these conditions.
15.1. Promising New Therapies
- Laser Therapy: Laser therapy can be used to treat certain types of tongue bumps, such as canker sores and benign tumors.
- Photodynamic Therapy: Photodynamic therapy involves using a light-sensitive drug and a specific wavelength of light to destroy abnormal cells.
- Biologic Therapies: Biologic therapies are drugs that target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process.
16. Understanding Diagnostic Procedures
When you visit a healthcare professional to diagnose the cause of tongue bumps, several procedures may be employed to accurately determine the underlying issue. These methods help differentiate between various conditions, ensuring appropriate treatment.
16.1. Common Diagnostic Tests
- Visual Examination: A thorough visual inspection of the tongue and oral cavity to identify the characteristics of the bumps.
- Medical History Review: Gathering information about your past and current health conditions, medications, and allergies.
- Palpation: Gently feeling the bumps to assess their texture, size, and consistency.
- Swab Culture: Collecting a sample from the bumps to test for bacterial, viral, or fungal infections.
- Biopsy: Removing a small tissue sample for microscopic examination to rule out more serious conditions like oral cancer.
- Blood Tests: Assessing vitamin levels, immune function, and signs of systemic diseases that may contribute to tongue bumps.
17. Managing Chronic Tongue Conditions
Dealing with chronic tongue conditions requires a comprehensive approach that involves lifestyle adjustments, medical treatments, and ongoing support. Effective management can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms.
17.1. Long-Term Strategies
- Adherence to Treatment Plans: Following the recommendations of your healthcare provider regarding medications, therapies, and follow-up appointments.
- Dietary Modifications: Identifying and avoiding foods that trigger flare-ups, while ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients.
- Stress Management: Implementing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling to manage stress levels.
- Regular Oral Hygiene: Maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine to prevent infections and promote healing.
- Support Groups: Participating in support groups to connect with others who understand what you are going through and share experiences and coping strategies.
18. Advanced Treatment Options
For those dealing with severe or persistent tongue bumps, advanced treatment options may be necessary to provide relief and prevent complications. These procedures are often performed by specialists and require careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks.
18.1. When to Consider Advanced Treatments
- Surgical Removal: Removing large or suspicious bumps through surgical excision.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing and destroying abnormal tissue using extreme cold.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors in cases of oral cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Administering drugs to kill cancer cells or slow their growth in cases of oral cancer.
19. The Future of Oral Health Research
Ongoing research in the field of oral health is continually advancing our understanding of tongue bumps and developing new and improved treatments. By staying informed about these developments, you can take a proactive role in managing your oral health and improving your overall well-being.
19.1. Promising Areas of Research
- Genetic Studies: Identifying genetic factors that may predispose individuals to certain tongue conditions.
- Immunotherapy: Harnessing the power of the immune system to fight oral cancer and other diseases.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup and other factors.
- Regenerative Medicine: Developing therapies to regenerate damaged tissue and restore normal function to the tongue.
20. Conclusion: Empowering Your Journey to Oral Health
Understanding why you get bumps on your tongue is the first step toward effective management and improved oral health. Whether it’s a minor irritation or a sign of an underlying condition, addressing tongue bumps with knowledge and care can lead to significant relief and peace of mind. At WHY.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the information and support you need to navigate your oral health journey with confidence. Remember, taking proactive steps and consulting with healthcare professionals are crucial for maintaining a healthy and happy tongue.
FAQ Section
Q1: What are the most common causes of bumps on the tongue?
A: Common causes include irritated taste buds, canker sores, infections, and transient lingual papillitis.
Q2: Are tongue bumps contagious?
A: Some tongue bumps caused by infections like herpes or syphilis are contagious, while others are not.
Q3: Can stress cause bumps on the tongue?
A: Yes, stress can weaken the immune system and contribute to conditions like canker sores and transient lingual papillitis.
Q4: What can I do to relieve the pain from tongue bumps?
A: Rinse with warm salt water, avoid irritants, and use over-the-counter pain relievers.
Q5: When should I see a doctor about bumps on my tongue?
A: If the bumps are painful, don’t heal after a few weeks, or are accompanied by other symptoms like fever or difficulty swallowing.
Q6: Can vitamin deficiencies cause tongue bumps?
A: Yes, deficiencies in vitamins like B12 and iron can cause bumps on the tongue.
Q7: How can I prevent tongue bumps?
A: Maintain good oral hygiene, watch your diet, avoid irritants, and manage stress.
Q8: What is transient lingual papillitis?
A: A common condition characterized by small, painful bumps on the tongue, often called “lie bumps.”
Q9: Can allergic reactions cause tongue bumps?
A: Yes, allergic reactions to certain foods or medications can sometimes manifest as bumps on the tongue.
Q10: Are bumps on the tongue ever a sign of oral cancer?
A: In rare cases, bumps on the tongue can be a sign of oral cancer. It’s important to see a doctor or dentist if you have any concerns.
If you’re experiencing persistent or concerning tongue bumps, don’t hesitate to reach out to the experts at WHY.EDU.VN. Our team of experienced professionals can provide personalized guidance and support to help you find the answers you need. Contact us at 101 Curiosity Lane, Answer Town, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (213) 555-0101, or visit our website at why.edu.vn to learn more. We’re here to help you take control of your oral health and well-being.